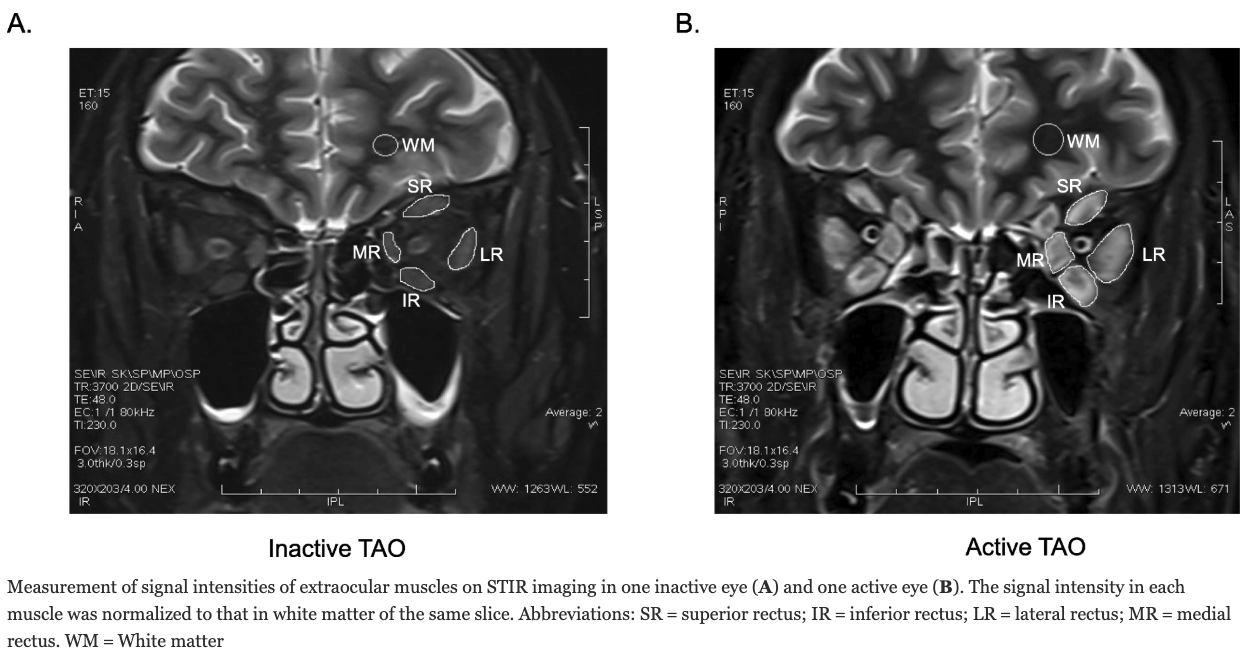
MRI STIR sequence for Disease activity in TAO
Research by : Qian Ge, Xiaohui Zhang, et al.
Summary by: GPT-4o
Edited and Curated by : Dr. Om J Lakhani
Summary of the Article
1. Title of the Article
Quantitative evaluation of activity of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy using short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence
2. First Two Authors followed by et al
Qian Ge, Xiaohui Zhang, et al.
3. One-line Summary of the Article
The study evaluates the use of MRI STIR sequences to quantify disease activity in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO) and proposes a signal intensity ratio (SIR) cut-off for staging the disease.
4. Six Key Points from the Article
- MRI STIR Sequence in TAO – The STIR sequence effectively differentiates between active and inactive TAO by highlighting water-containing inflammatory changes in extraocular muscles.
- Signal Intensity Ratio (SIR) Analysis – The study measured SIRs in four extraocular muscles and found significantly higher values in active TAO compared to inactive TAO and controls.
- Correlation with Clinical Activity Score (CAS) – After adjusting for age and smoking, SIRs strongly correlated with CAS, confirming their predictive value in determining disease activity.
- Cut-off Value for Diagnosis – An SIR of >2.9 in the inferior rectus muscle demonstrated the best diagnostic performance for identifying active TAO.
- Validation in a New Cohort – The proposed SIR cut-off was validated in a separate group of TAO patients, showing high specificity (100%) and sensitivity (93.75%) for staging active TAO.
- Clinical Implications – Using STIR-derived SIRs can improve TAO staging and guide treatment decisions, such as the timely initiation of immunosuppressive therapy.
5. Practical Take-home Message
MRI STIR imaging provides a reliable, non-invasive method for staging TAO. A cut-off SIR value of >2.9 in the inferior rectus muscle can serve as a useful diagnostic tool to differentiate active TAO from inactive disease, potentially aiding treatment decisions.
6. Citation in Vancouver Format
Ge Q, Zhang X, Wang L, Fan Y, Huang Q, Yao N, et al. Quantitative evaluation of activity of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy using short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021;21(226). doi:10.1186/s12902-021-00895-3.