-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Q. What are the exact anatomical effects of maternal Hypothyroidism on the fetal brain?
- Reduced neuronal differentiation
- Reduced synapse formation
- Reduced myelin formation
- Reduced axonal and dendritic growth
- Reduced astrocyte development
-
Q. Which is more critical for fetal development- T4 or TSH?
- Free T4 and T3 are essential for fetal development
- TSH is essential for maternal well being
-
Q. Does high T4 affect the fetal brain?
- Both high and low T4 has an adverse effect on fetal brain development
-
Q. What is a complete form of the CATS study?
- Controlled antenatal thyroid screening
-
Q. What was the design for the CATS study?
- Women <15 weeks of gestation TFT was done
- Women with Free t4 <2.5 th percentile and TSH >97.5 percentile were treated with 150 mcg of LT4
- IQ of the child was studied at 3 years
- In the control group- TFT sample was taken and stored and analyzed after delivery
-
Q. What were the results of the CATS study?
- Antenatal screening (at a median gestational age of 12 weeks 3 days) and maternal treatment for Hypothyroidism did not improve cognitive function in children at 3 years of age.
-
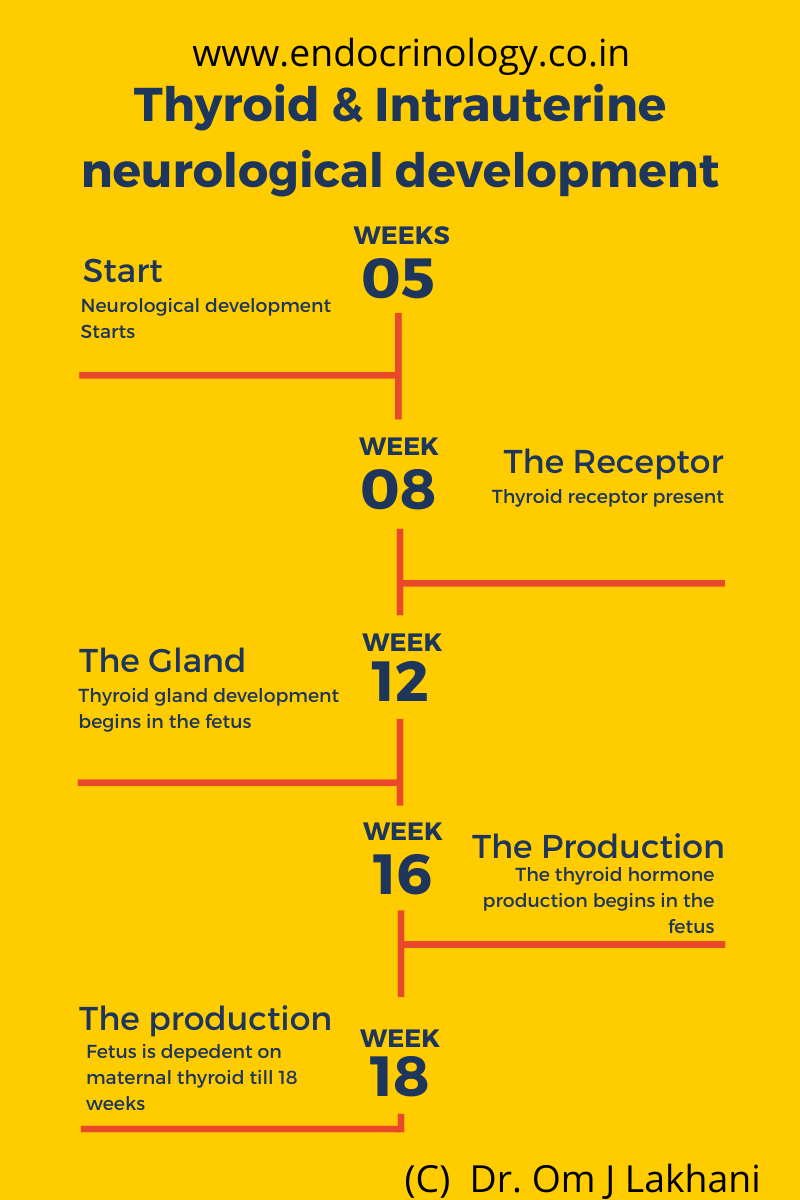
Q. Summarize the intrauterine timings in relation to the thyroid and neurological development?
- Neurological development – starts at 5 weeks
- Thyroid receptor present by 8 weeks
- Thyroid gland development – 12 weeks
- Thyroid hormone production – 16-18 weeks of gestation
- Hence from 5 weeks to 18 weeks – the fetus is dependent on the maternal thyroid
-
Q. What are the neurological manifestation of fetal Hypothyroidism?
- Mental retardation and low IQ
- Developmental delay
- Spasticity
- Deafness
-
Q. How is the fetus protected from an excessive amount of maternal T4?
- By type 3 deiodinase present in the placenta
-
- Thyroid is essential for brain development in the first 1000 days of life, including the antenatal period
-
Q. Which affects the fetal brain- T4 or T3?
- T3
- Fetal neurological tissue has local deiodinase 2, which converts T4 to T3
-
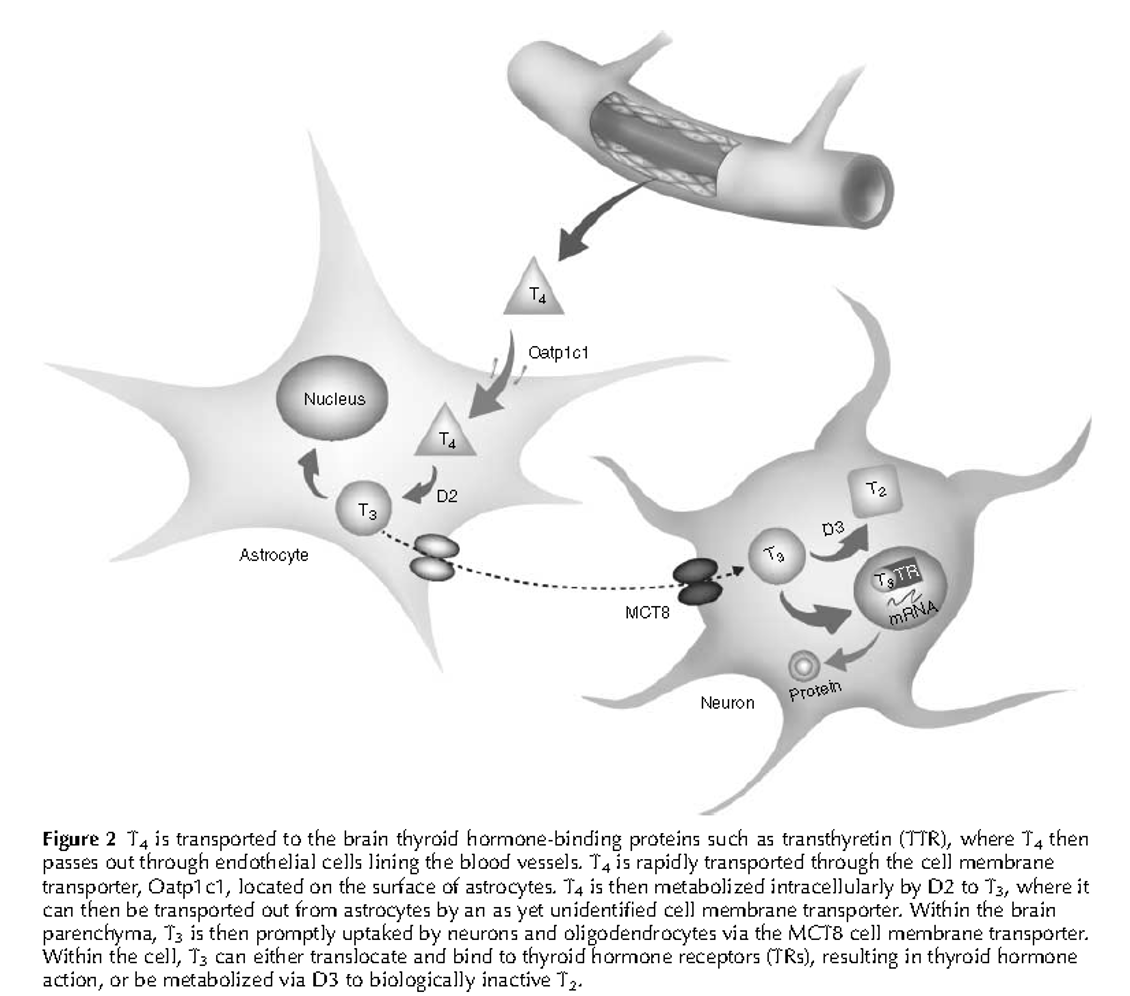
Q. Which are the various thyroid hormone transporters in the fetus?
- MCT8 and 10
- OATP2 and OATp3
- LAT1 and LAT2
-
Q. Describe with diagram the transport process of thyroid hormone in the fetus?
-
Q. What is the importance of MCT8?
- MCT8 is critical for T3 to enter the neurons
- Hence MCT8 deficiency produces a neurological disorder called Allan-Herndon Dudley syndrome
-
Q. What neurological outcomes are studied in various studies in relation to fetal brain and thyroid?
- IQ
- Risk of ADHD
- Risk of Autism
- Risk of schizophrenia
- Gray matter volume and morphology
-
Q. What is the Generation R study?
- Study published in Lancet
- Showed that both high and low T4 is associated with lower IQ in children
- This was the population-based prospective cohort study
-
Q. How much is IQ reduction seen in infants of mothers having untreated Hypothyroidism?
- 7 point reduction in IQ
- This is from a study by Haddow et al
-
Q. Is lower maternal T4 associated with poor brain outcomes?
- Prolonged low T4 is in mother is associated with poor neurological outcomes
-
**Iodine nutrition and pregnancy **
-
Q. What is the recommended intake of iodine during pregnancy?
- 250 mcg/day
-
Q. How is iodine deficiency assessed?
- Using urinary iodine concentration
- Sufficient iodine status is determined by UIC of 150-250 mcg/l
-
Q. How much gap must be there between thyroid supplementation and iron supplementation?
- At least 4 hours
-
Q. What should be the iodine intake during breastfeeding?
- 250 mcg/day (some recommend 290 mcg/day)
-
Q. Why is iodine deficiency during pregnancy so important?
- Because it is the leading cause of preventable brain damage
-
Q. When does iodine deficiency produce neurological cretinism, and when does it produce myxomatous cretinism in infants?
- Iodine deficiency in early pregnancy – neurological cretinism
- Iodine deficiency later in pregnancy – myxomatous cretinism
Please consider donating to "Notes in Endocrinology" to keep us going. Please visit our DONATION page to know more