- Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
Support us:
- Support us by purchasing our book - Click here for more details: Volume 1- THE BEST OF NOTES IN ENDOCRINOLOGY BOOK SERIES
- Support you by Becoming a YouTube member (Click here)
-
Note: for Hashimoto's encephalopathy 1 - please see separate notes (Coming soon)
-
Q. Enlist the neurological manifestations of hypothyroidism in adults ?
- Myxedema coma
- Cognitive impairment (Dementia)
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Peripheral neuropathy – including Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Hypothyroid myopathy
- Sensorineural hearing loss
-
Q. What are the neurological manifestation of Cretinism (congenital hypothyroidism) ?
- Intellectual impairment
- Delayed motor milestones
- Kocher- Debre- Semelienge syndrome – hypothyroid myopathy
- Sensio neural hearing loss
- Strabismus
-
Q. What is myxedema madness ?
- Psychosis seen with severe hypothyroidism
-
Q. Cognitive impairment (dementia) in hypothyroidism is cortical or subcortical ?
- It is mainly subcortical
-
Q. Is Subclinical hypothyroidism associated with dementia ?
- Results are conflicting
-
Q. What other types of psychiatric manifestations are common in hypothyroidism?
- Depression and anxiety are common features of hypothyroidism
-
Q. Should cognitive impairment in elderly be screened for hypothyroidism?
- Yes
- Elderly with cognitive impairment must be screened for hypothyroidism based on AAN guidelines
-
Q. Is there a link between Parkinsonism and Hypothyroidism ?
- Again, conflicting data
- However patient with Parkinsonism who does not respond to treatment must be screened for hypothyroidism
- Also Levodopa reduces TSH and hence this care must be taken while screening
-
Q. Is hypothyroidism commonly associated with cerebellar ataxia ?
- Yes
Hypothyroidism and Depression
Q. What is the relation between Serotonin levels and hypothyroidism ?
- #Clinicalpearl
- Serotonin has a feedback loop with TRH. It suppresses TRH
- T3 in the brain increases serotonin levels
-
Q. Do larger studies show any relation between depression and hypothyroidism?
- According to a meta-analysis- some of the larger studies have shown no correlation between depression and hypothyroidism
-
Q. What is the biggest bias with these studies ?
- These studies by its nature, excludes patients already on LT4 and diagnosed to have hypothyroidism previously
- The remaining people are those who probably did not have an indication for treatment in the first place
-
Q. Is there a relationship between any thyroid-related polymorphism and depression?
- Yes
- A seminal study on this topic found a strong correlation between polymorphisms in Deiodinase type 2 (DIO2) and depression in hypothyroid Caucasian females
-
Q. Can you elaborate more on this?
- In the CNS- only type 2 deiodinase is present to convert T4 to T3
- Subanalysis of various meta-analyses done for T3/T4 combination therapy has shown that a particular subset of patients having a polymorphism rs225014 in DIO2 have benefits in terms of T3 and T4 combination
- This polymorphism was present in 12% of subjects
- There is no biochemical test to identify this subset of a patient and can only be identified with genetic testing
-
Q. Is there any other polymorphism that may have a potential association?
- Polymorphism in OATP1C1, which helps transport T4 to the brain, may be associated with depressed mood and other psychological features
-
Q. Is there a relationship between thyroid autoimmunity and depression?
- some studies have shown a correlation between Anti TPO positivity and depression
- This is especially true since Post partum thyroiditis is known to present as depression
-
Q. Despite adequate control of TSH biochemically, do some patients with hypothyroidism continue to have a poor sense of well-being?
- Yes
- This has been shown in several studies in patients treated with LT4
- In fact, some patients on LT4 may have worse psychological outcomes
-
Q. What is cycle of misattribution?
- This is one of the reasons why patients with hypothyroidism may not receive clinical response with Levothyroxine]] treatment
- Patients having symptoms of depression- tested for hypothyroidism as per protocol - found to have Subclinical hypothyroidism- treatment started, but to start Subclinical hypothyroidism was NOT the reason for depression!
- This is a cycle of misattribution
-
Q. Does treatment with LT4 improve the mood?
- There are no convincing placebo-controlled trials to show that there is a clear benefit in the mood with treatment with LT4
- Only one placebo-controlled trial by Meier et al. have shown some benefit inpatient in whom TSH was >12
-
Q. Is the combination of T3 and T4 having benefits?
- This is an area of controversy
- Large meta-analyses have shown no benefit, while some small studies have shown benefit
- The exact dose and ratio of T3/T4 is different in different studies and hence making it difficult to interpret
-
Q. Is overcorrection associated with adverse psychological outcomes?
- Largely- trials have not shown this to be true
-
Q. Does adding T3/T4 improve the effectiveness of anti-depressants?
- Again, this is a controversial area with no clear consensus in either direction
- Larger trials have shown mixed results- especially with T3
- At present, there is no benefit of using LT4 or T3 for this purpose
-
Q. What are the take-home messages from hypothyroidism and depression?
-
- There is no clear relation between LT4 replacement and improvement in mood with patients with hypothyroidism
-
- A lot of these patients may have a cycle of misattribution - a patient with depression having the symptoms attributed to hypothyroidism
-
- T3/T4 combination may or may not have the benefit
- It is beneficial in patients having a functional polymorphism in the DIO2 (type 2 deiodinase) enzyme
-
-
Evidence-Based Use of Levothyroxine/Liothyronine Combinations in Treating Hypothyroidism: A Consensus Document
-
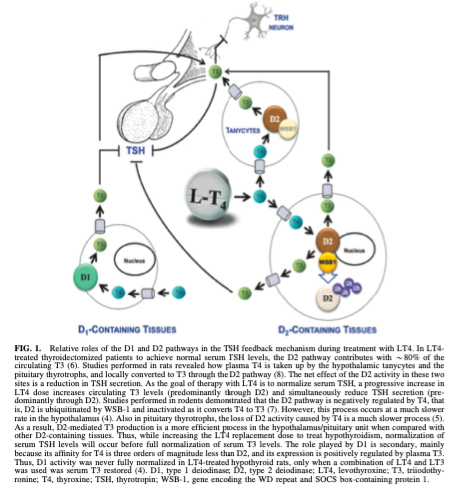
Q. What happens to the T3 when we treat hypothyroidism patients with LT4?
- Studies in humans have shown that the use of LT4 for treating hypothyroidism leads to normalization of TSH, but abnormal FT4/FT3 ratio.
- The FT3 is not normalized like it should be because of LT4
-
Q. Where are the Type 1 deiodinase and Type 2 deiodinase found in the human body?
- Type 1 deiodinase- Liver and Kidney
- Type 2 - is found in the heart, skeletal muscle, CNS, fat, thyroid, and pituitary
-
Q. Of the above 2 - which contributes most to the T3 levels?
- Type 2 deiodinase contributes 80% of the T3 levels
-
Q. So why does treatment with LT4 lead to pooer T4/T3 ratio?
- LT4 given is taken up by the hypothalamus and pituitary - converted to T3 by the local D2, and then it normalizes TSH rapidly
- However, the above correction occurs faster compared to the normalization of T3 levels in the peripheral circulation
- Hence an adequate T3 level is never achieved before the TSH is normalized
-
Q. Which specific Type 2 deiodinase polymorphism has produced this debate?
- Thy92 Ala
-
Q. What effects of the thyroid hormone are thought to occur via a non-canonical or non-thyroid receptor pathway?
- Effect on cancer growth
-
Q. What are the issues with the clinical trial with T3/T4 combination?
- The suitable patients may not have been included
- The suitable patients include those who are dissatisfied with the T4 replacement
-
Q. What is the pharmacological equivalence between T3 and T4?
- 1 T3 = 3 T4
- i.e., 100 mcg of T4 = 33.3 mcg of T3
- 40 mcg of T3 = 115 mcg of T4
-
Q. What are the problems with T3 assays?
- At low concentration, the T3 or FT3 immunoassays are less reliable
- It is also affected by the patient factors
- Patients on dietary restriction have lower levels
- Patients with illness may have lower levels
- Age
- Time of the day
-
Q. If given as monotherapy, how is T3 given?
- it is given three times a day
- Typically, 10 mcg TDS would be around 120 mcg of T4
- Trials have used twice a day T3 generally because of patient compliance issue
-
Q. What is the half-life of T3?
- 22 hours
-
Q. In our terms, how much thyroid hormone is produced by the thyroid gland?
- 100 mcg of T4 is produced, and the normal thyroid gland produces about five mcg of T3
- This is about a 14:1 ratio
-
#Clinicalpearl: Slow release T3 preparations are required to solve the problem of the T3 and T4 combination
-
Q. What happens to TSH with T3 monotherapy is given?
- Studies have shown that with T3 monotherapy, the TSH levels tend to be a little lower
- Fluctuations are also more
- Lower TSH]] here may not represent overcorrection
-
Q. Which are two critical psychological outcomes attributable to hypothyroidism?
- Two outcomes attributable to hypothyroidism include
- Emotional susceptibility
- Tiredness
- Depression and Anxiety are NOT attributable to thyroid dysfunction
- Two outcomes attributable to hypothyroidism include
-
Q. What is the top psychological concern of patients with hypothyroidism?
- Fatigue is the chief concern in patients with hypothyroidism
- General fatigue
- Physical fatigue
- Mental fatigue
- Fatigue is the chief concern in patients with hypothyroidism
-
- Thyroid related QoL indices tend to perform better compared to general QoL indices like SF-36 etc
- For fatigue specifically, thyroid-related fatigue may be different from other fatigues!
-
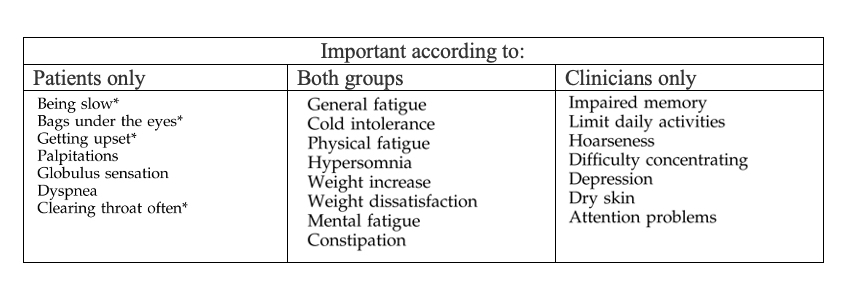
Q. In hypothyroidism, what is the difference between patient-perceived symptoms and clinician-perceived symptoms ?
-
Why are our hypothyroid patients unhappy? Is tissue hypothyroidism the answer?
- Zulewski symptom score for hypothyroidism

- Score ≥ strong correlation with hypothyroidism
- <2 - less relation
- Zulewski symptom score for hypothyroidism
-
Q. Which two tests should be done to assess tissue level hypothyroidism and its correlation with hypothyroidism?
- lipid profile]]
- Creatine kinase]]
- They have correlation with symptoms