-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Q. What is the definition of Familial isolated pituitary adenoma (FIPA)?
- Stiles et al. define FIPA as "A term used to identify a genetic condition with pituitary tumors without other endocrine or other associated abnormalities." [1]
-
Q. Name the various germline mutation seen with Pituitary tumors?
- MEN – Menin (MEN1), CDKN1B (MEN4)
- FIPA - AIP, GPR101 (XLAG)
- SDH related pituitary adenoma- SDHA, B, C, D
- Carney’s complex related- PRKAR1A
- Neurofibromatosis – NF1
- Pituitary blastoma- DICER1
-
Q. What are two broad categories of Familial isolated pituitary adenoma (FIPA)?
- FIPA with AIP mutation
- FIPA without AIP mutation
-
Q. What is fullform of AIP ?
- Aryl hydrocarbon interacting protein
-
Q. What was the basis of the origin of FIPA?
- In a search to identify tumors of the pituitary not having MEN1 or Carney’s complex lead to the discovery of FIPA
-
Q. What is homogenous FIPA, and what is heterogenous FIPA?
- Homogenous FIPA- same pituitary tumor syndrome amongst family members
- Heterogenous FIPA – different pituitary tumor syndromes
-
Q. Describe the frequency of various pituitary tumors in FIPA?
- Prolactinoma- 37%
- Somatotropinoma – 35%
- NFPA -14%
- Somatolactotropinoma – 6.4%
- Cushing’s disease 2.9%
- Less than 1-2% :
- gonadotropinoma
- Plurihormonal
- thyrotropinoma
-
Pearl
- Prevalence of prolactinoma compared to the general population is slightly lower
- However, it is still the most common
- Somatoropinoma has a much higher prevalence compared to the normal population
-
Q. Loss of heterogenicity in which region has been associated with somatotropinoma in the general population?
- LOH in 11q13 is commonly associated with somatotropinoma
-
Q. What is the penetrance of AIP mutation?
- Variable penetrance – 20%
-
Q. Does pituitary adenoma with AIP mutation occur at a younger age?
- Yes
-
Q. Is gigantism more common with AIP mutation?
- Yes
-
Q. Is Non-functioning pituitary adenoma (NFPA) in FIPA more aggressive?
- Yes
-
Pearl
- Pituitary adenomas with FIPA are
- Occur at a younger age
- More aggressive
- Poor response to treatment
- Larger size
- Even within FIPA, those with positive AIP mutation have more significant of the above features compared to AIP negative ones
-
Q. Are AIP mutations germline or somatic?
- Germline only
-
Pearl
- FIPA – overall – prolactinoma most common
- FIPA with AIP mutation – Somatotropinoma is most common
-
Q. AIP mutation is more common in males or females?
- More in males
-
Q. Is pituitary apoplexy more common in AIP patients?
- Yes
-
Q. Are somatoropinomas with AIP mutation relatively resistant to treatment with Somatostatin analogs?
- Yes
-
Q. What is the mode of inheritance?
- It is autosomal dominant
-
Q. What % of pituitary adenoma are FIPA?
- 2-3%
-
Q. What is the role of the AIP gene?
- Exact role is not known
- But studies in mice have shown that AIP -/- tend to die in-utero because of defective cardiac development
- When Aip +/- develop a disease similar to humans – aggressive somatotropinoma
-
Q. How common is AIP mutation in FIPA patients?
- 25% of FIPA patients have AIP mutation
-
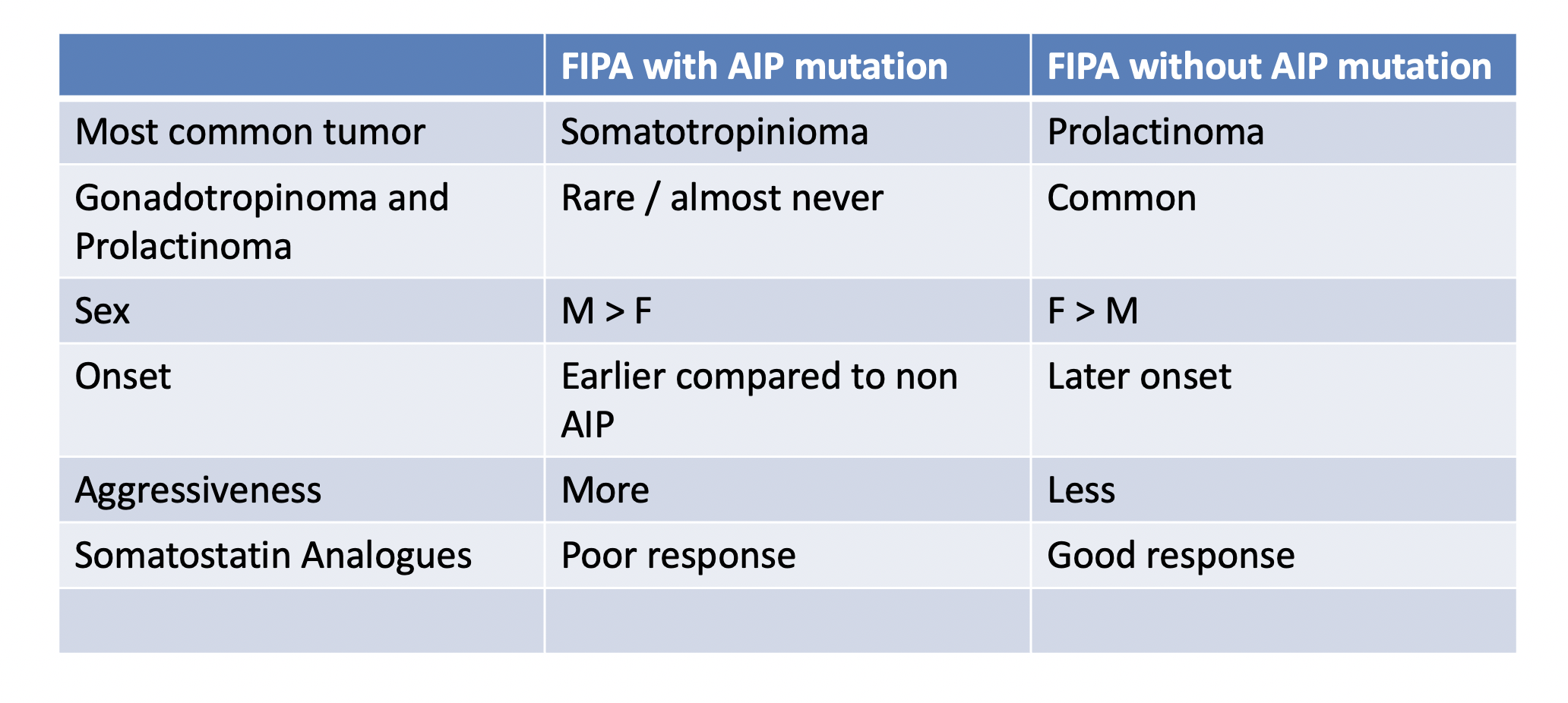
Q. What is the difference in patients of FIPA with AIP mutation and without?
-
Q. Give an outline for genetic testing in a patient with Pituitary adenoma?
-
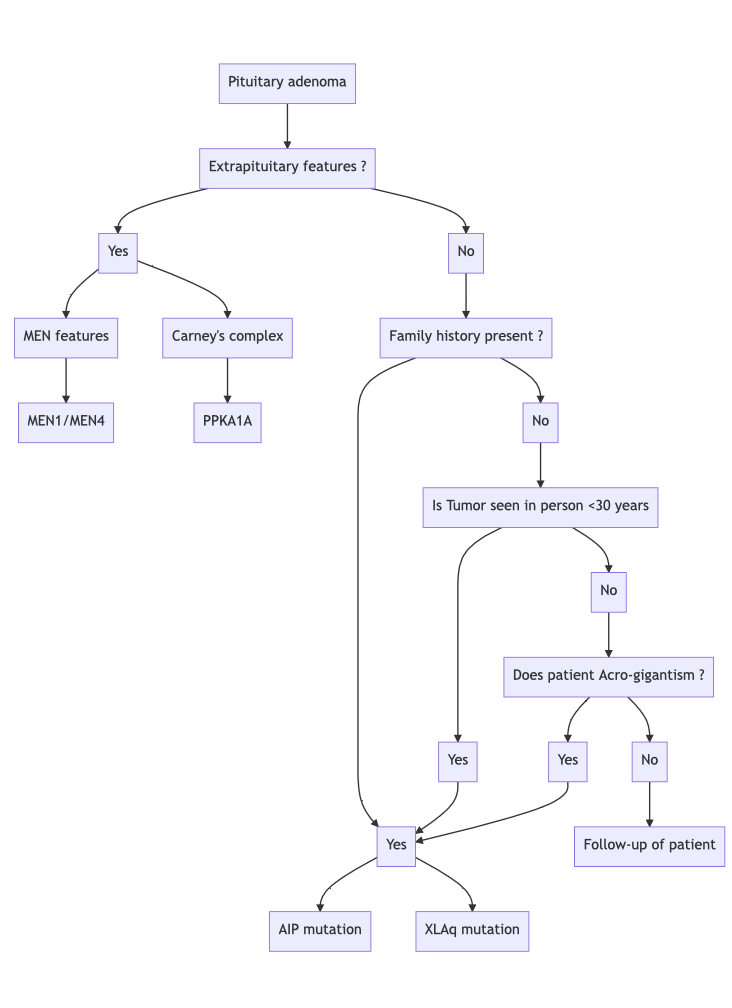
-
*please read as XLAG instead of XLAq (Apologies for the typo)
-
-
Q.What are the tests done in patients screened to be AIP mutation-positive?
- Baseline
- History, signs and symptoms, clinical examination
- Baseline pituitary hormones
- IGF1 and oGTT (for Growth hormone)
- Baseline MRI
- Baseline
Ref: Stiles CE, Korbonits M. Familial Isolated Pituitary Adenoma. [Updated 2020 May 28]. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278949/ ↩︎