-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Other Genetic anomalies
-
Q. What is Macrozoospermia?
- It is a form of Teratospermia
- It is because of the lack of an enzyme called Aurora kinase C
- This enzyme is responsible for the cell division
- Because of the lack of this enzyme- the sperms have extra chromosomes, which gives it a large head
- This abnormal sperm often leads to infertility or miscarriage because of extrachromosomal material
-
Q. What is globozoospermia?
- This is also a form of Teratospermia
- In this, the head of the sperm is a globe in shape instead of oval because of the lack of the acrosomal cap.
- This is because of a genetic defect in DPY19L2 gene
-
Sperm Retrieval
-
Q. What are the various techniques for Sperm retrieval?
- PESA - Percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration
- MESA - Microsurgical epididymal sperm aspiration
- TESA - Transcutenous epididymal sperm aspiration
- TESE - Transcutenous epididymal sperm extraction
- MicroTESE
- Vasal Aspirate
-
Q. Which of these techniques is good for obstructive azoospermia?
- Any of the above may be used for obstructive Azoospermia
-
Q. Which is better for Non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA)?
- MicroTESE
-
Other points
-
Q. What are the grades of Varicocele?
- Grade 1- only on cough impulse
- Grade 2- palpable not visible
- Grade 3- visible
-
Q. When is ICSI preferred over conventional IVF?
- Sperm count - <2 million
- Motility - <5%
- Normal morphology <5%
- Poor sperm – cervical mucous interaction
- Antisperm antibody
-
Q. What is the secular trend in sperm count?
- There is a secular trend towards falling sperm count
-
Q. How many semen analyses must be done before drawing any conclusion?
- 2-3 samples over 2-3 months
-
Q. Does the WHO 2010 data for Semen analysis include Indian patients?
- No
-
Q. Which is the most important parameter in the WHO semen analysis according to Infertility specialists?
- Most important parameter is morphology
- Morphology > 4% is associated with sperm count
- If overrides other factors
-
Q. What is leuckocytospermia?
- It is peroxide positive WBC >10 ^ 6 /ml
- This generally gives poor results if there are WBC in the sperms
-
Q. What is the success rate after ICSI?
- 40%
-
Q. What is the effect of reactive oxygen species in sperms?
- It causes DNA fragmentation
- It may lead to idiopathic male infertility
-
Q. What is IMSI?
- Intracytoplasmic morphologically selection sperm injection
-
Q. What is P-ICSI?
- Petri Dish ICSI
- Use of hyaluronic acid-binding to select sperms for ICSI
-
Q. What test must be considered for patients with repeated IVF failure?
- Test for DNA fragmentation
-
Q. What is semen preparation?
- It is washing of semen done to remove debris, WBC, bacteria, etc
- It is ideally done within 30 min of ejaculation
-
Q. Name some semen preparation techniques?
- Swim-up
- Density gradient centrifugation
- Percoll gradient
-
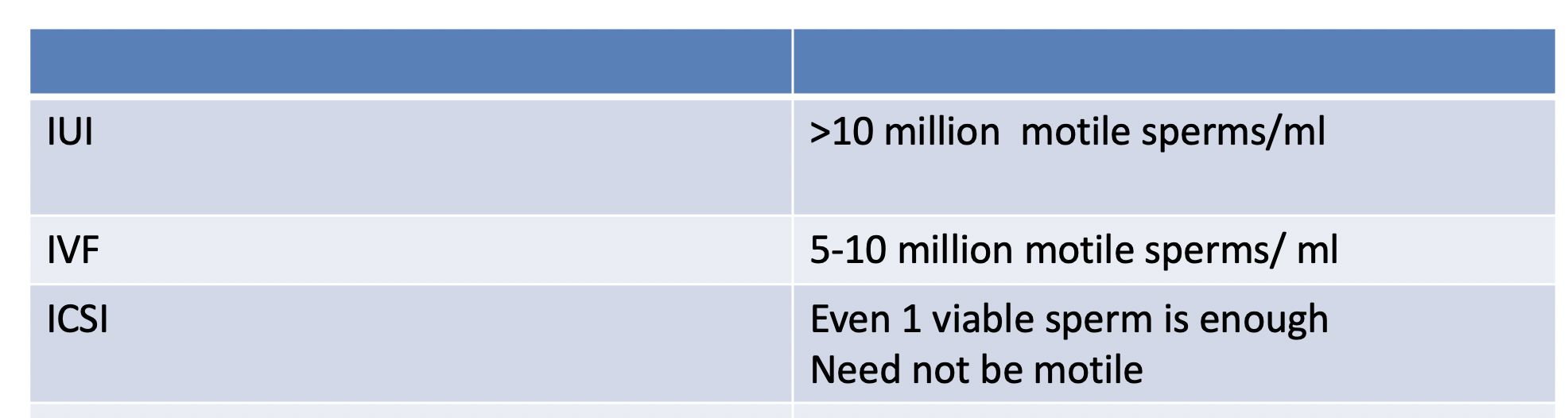
Q. What is the sperm cutoff and various ART?
-
Q. Which is the oldest sperm function test?
- Sperm – cervical mucus interaction
- Not used much these days
-
Q. What is the investigation of choice for immotile sperm?
- Hypoosmotic sperm swelling
-
Q. When should genetic testing be considered for male infertility?
- When sperm count <10 million / ml
-
Q. Which mutation is specifically associated with azoospermia?
- Yq microdeletion = AZF – azoospermia factor deleted
-
Q. Which is the newest deletion recorded?
- Gr/gr deletion- increase risk of oligospermia and also testicular germ cell tumors
-
Q. Should varicocele with OAT/Azoospermia be treated?
- Yes
- Evidence suggests there is improvement in sperm parameters and fertility after Surgery of varicocele
-
Q. How does varicocele impact male fertility?
- It increases reactive oxygen species and causes DNA fragmentation
- it reduces the sperm count
- It leads to smaller size testis and also lowers the testosterone