-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Q. What suppresses the GnRH during childhood ?
- GABA and opiod peptides
-
Q. What enhances GnRH secreation ?
- Glutamate and Kisspeptin
-
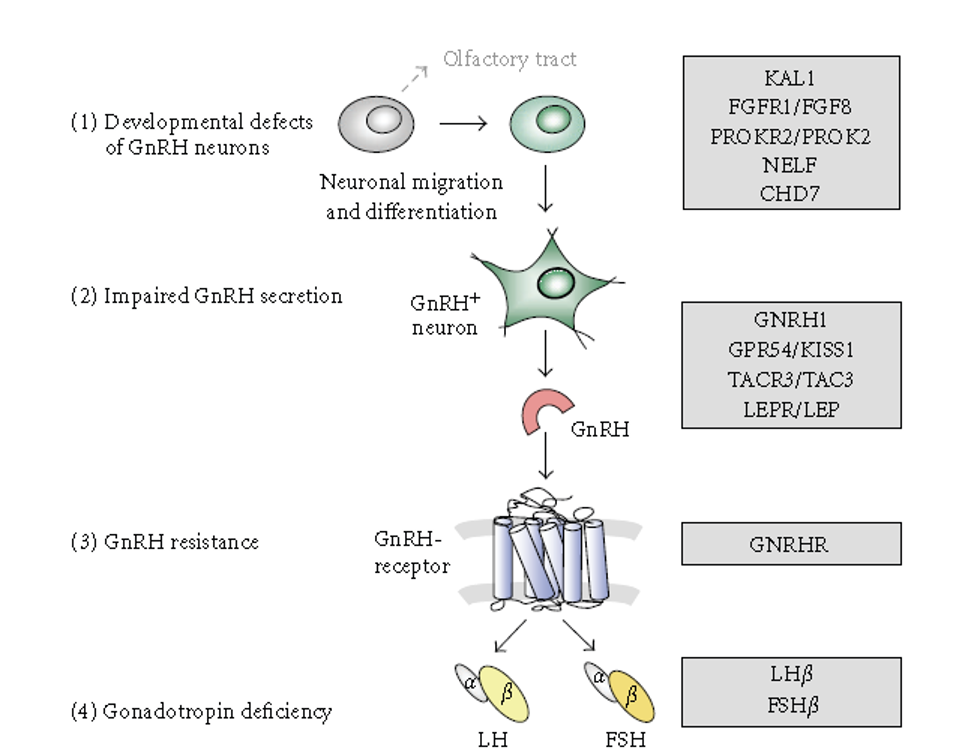
Q. Summarize the potential genetic defects that lead to IHH ?
-
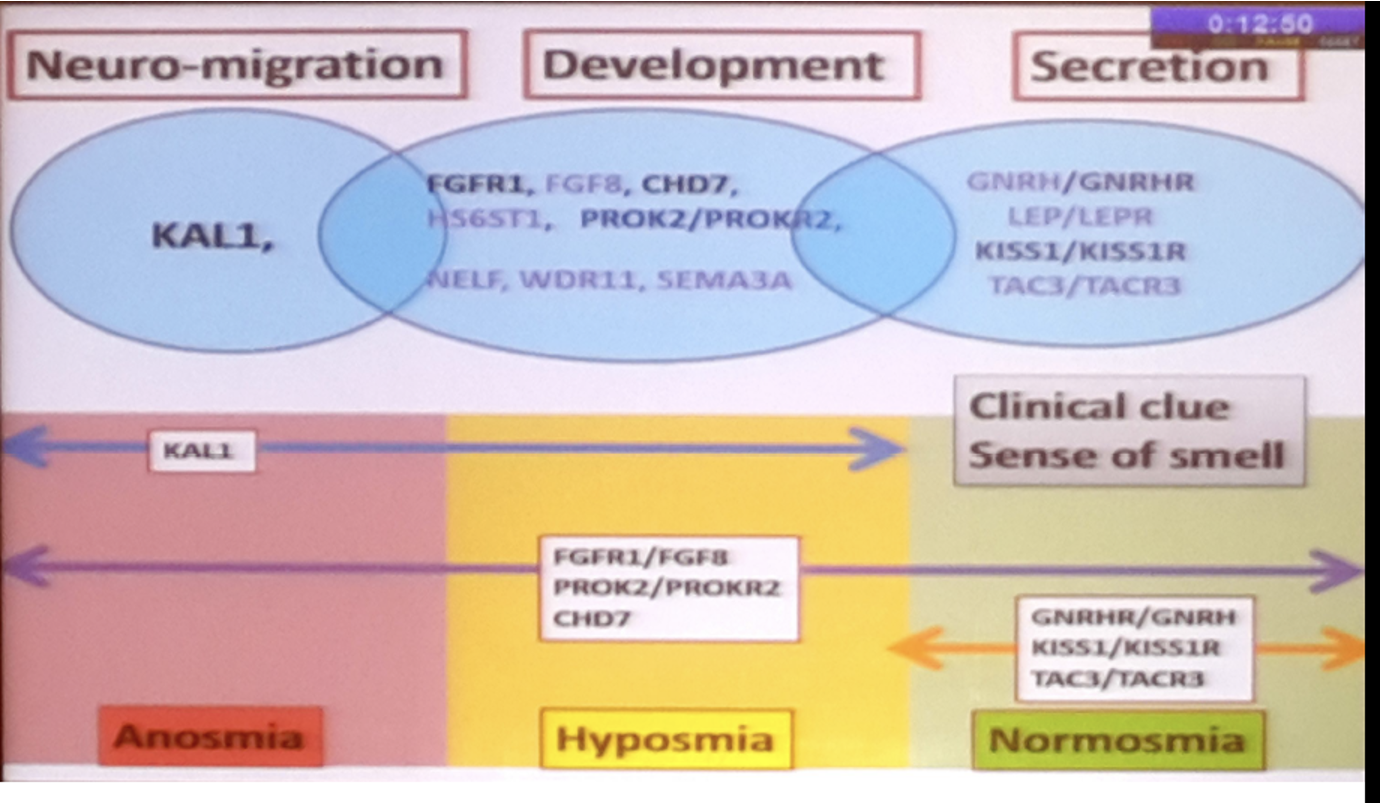
Q. Classify the genetic defects in IHH based on whether they are anosmic, hyposmic or normosmic ?
-
Q. How common are normosmic and anosmic IHH ?
- Anosmic- 50-52%
- Normosmic- 48-50%
-
Q. Which is the most common cause of Normosmic IHH ?
- Inactivating mutation in GnRH receptor
- It is also the most common AR form of IHH
-
**DEFECT IN GNRH DEVELOPMENT AND MIGRATION **
-
Q. What are classical Clinical features of KAL1 mutation ?
- X linked
- Ansomia
- Bimanual synkinesia
- Unilateral renal agnesis
- Anosmin 1 defect
- Poor migration of GnRH neurons
-
Q. How do mutation in FGF8 and FGFR1 present ?
- AD inheritance
- Cleft lip/cleft palate
- May be Normosmic or anosmic
- Variable degree of hypogonadism which often reverses
- Dental abnormalities
- Ear abnormality
- Helps in development of GnRH neurons in its niche
-
Q. How do PROK2 or PROKR2 present ?
- AD or AR
- Normosmic or anosmic
- Helps in development and migration of GnRH neurons
-
Q. How do defect in CHD7 present as ?
- Presents as CHARGE syndrome
- C - Coloboma or iris
- Heart problems
- Atresia choane
- R- retardated growth and development
- G- genital abnormality
- E- ear abnormality
-
Q. What is choanal atresia ?
- Choanal atresia is a congenital disorder where the back of the nasal passage (choana) is blocked, usually by abnormal bony or soft tissue (membranous) due to failed recanalization of the nasal fossae during fetal development.
-
**DEFECT IN GNRH SYNTHESIS AND RELEASE **
-
Q. How do mutation of GPR54/KISSR or KISS1 present ?
- Presents with Normosmic IHH
- GPR54/KISSR (receptor) mutation are known
- But KISS1 (ligand) mutation are not known
- They are Autosomal recessive
-
**DEFECT IN GNRH FUNCTION **
-
Q. How do patients with LH beta defect present ?
- Males- absent puberty and azospermia
- Females- large ovaries with normal/late menarche and oligomenorrhea due to anovulatory cycles
-
Q. How do patient with FSH-beta mutation present as ?
- Females – primary amenorrhea and lack of secondary sexual characterstics
- Male- Azoospermia
-
Q. Which genetic test to do if child has cleft lip or cleft palate ?
- FGF8 or FGFR1
-
Q. What about bimanual synkinsea ?
- KAL1
-
Q. When is there is obesity with Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (Congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism) ?
- Leptin
- Leptin receptor
- PCSK1
- Prader Willi
- Bardet Biedel
-
Q. IHH with hearing defect ?
- CHD7- CHARGE syndrome
- SOX10
- IL17RD
-
Q. IHH with Split-hand foot malformation ?
- FGFR1
-
Q. Enlist the 6 genes involved in Kallmann syndrome (IHH with anosmia) ?
- KAL1- X linked
- FGF8
- FGFR1- AD with incomplete penetrance
- PROK2
- PROK2R- AR/AD
- CHD7
Please consider donating to "Notes in Endocrinology" to keep us going. Please visit our DONATION page to know more