-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Q. Why is the timing of testosterone defect important in congenital abnormalities of primary hypogonadism?
- Defect in 1st trimester- male external genitalia would not be adequately formed – ambiguous genitalia or female external genitalia
- Normal Trimester in the first trimester but defective in 3rd trimester - micropenis at birth
- Normal Testosterone in utero, Testosterone defect before puberty- absent secondary sexual characteristic, Eunhacnoid proportions, gynecomastia
- Testosterone defect after puberty – normal virilization, gynecomastia, testicular atrophy, reduced libido, infertility
-
Q. What is the typical phallus length in prepubertal testosterone deficiency?
- Stretched penile length <8 cm
-
Q. What are the features of Prepubertal testosterone deficiency?
- Eunuchoid proportions
- Absent spermarche
- Small testis
- Small phallus - <8 cm
- May have gynecomastia
- Absent acne
- Absent temporal hair recession
- High pitched voice
- Body composition - female
- Female eschaton
- Reduce muscle mass
- Absent pigmentation and rugosity of scrotum
-
Q. What are the features of eunuchoid proportions?
- lower segment > Upper segment by 2 cm
- Arm spam > height by 5 cm
-
Q. Summarize the clinical features of male hypogonadism based on the age of onset and whether it is primary or secondary hypogonadism?
Prepubertal onset of hypogonadism
| Clinical feature | Primary hypogonadism | Secondary hypogonadism |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced libido | + | + |
| Infertility | ++ | +/- |
| Gynecomastia | ++ | - |
| Small testis | ++ | ++ |
| Small penis | + | + |
| Eunuchoid proportions | + | + |
| Reduced muscle mass | + | + |
| Reduced body hair | ++ | ++ |
Post-pubertal onset
| Clinical feature | Primary hypogonadism | Secondary hypogonadism |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced libido | + | + |
| Infertility | ++ | +/- |
| Gynecomastia | ++ | - |
| Small testis | + | + |
| Small penis | - | - |
| Eunuchoid proportions | - | - |
| Reduced muscle mass | + | + |
| Reduced body hair | +/- | +/- |
Pre-pubertal versus post pubertal onset hypogonadism
| Clinical feature | Pre-pubertal | Post-pubertal |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced libido | + | + |
| Infertility | +/- | +/- |
| Gynecomastia | +/- | +/- |
| Small testis | ++ | + |
| Small penis | + | - |
| Eunuchoid proportions | + | - |
| Reduced muscle mass | + | + |
| Reduced body hair | + | +/- |
-
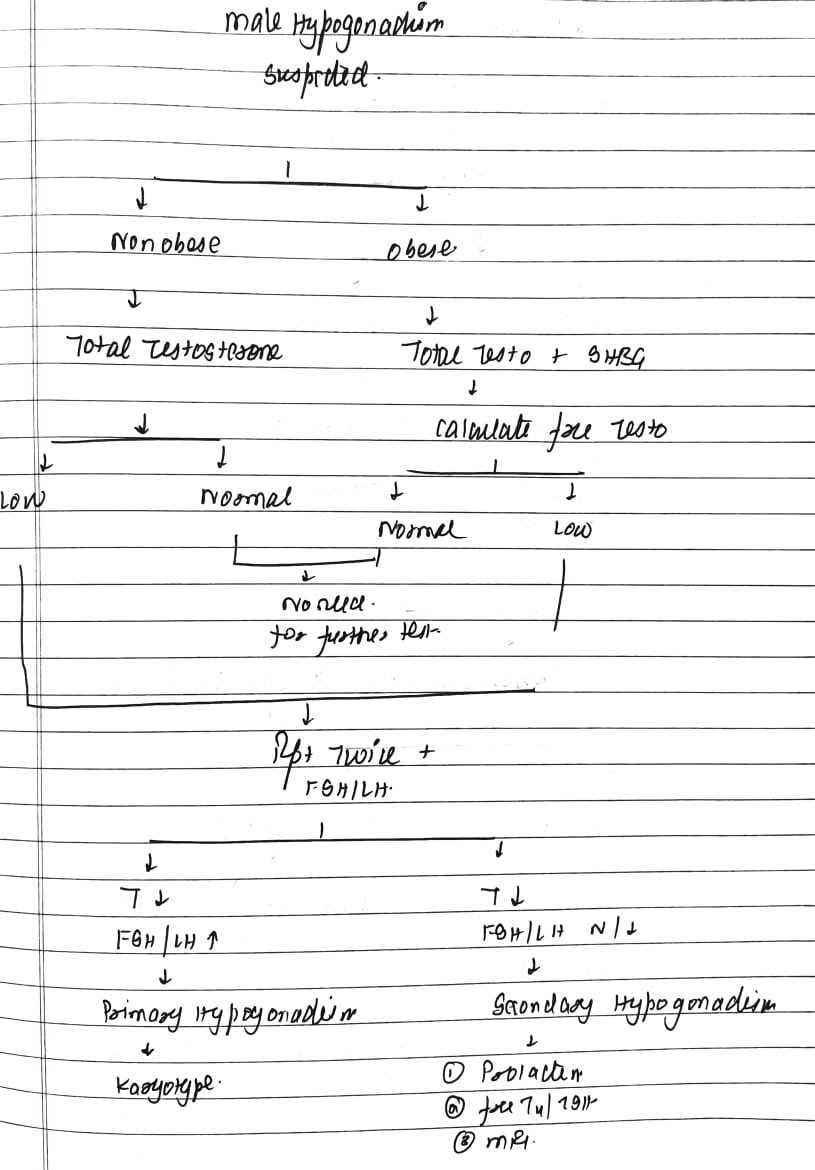
Q. Give the algorithm for an approach to male hypogonadism?
-
Q. What are the indications for doing MRI in male hypogonadism?
- Increase prolactin
- Male <40 with testosterone <250 ng/dl
- Male >60 years with testostetrone <150 ng/dl
-
Q. In which conditions is SHBG tested?
- Obesity – SHBG reduced
- Aging- SHBG increased
-
Q. In which cases is SHBG increased?
- Aging
- Estrogen
- Hyperthyroidism
- Anti-epileptics
- HIV
-
Q. in which cases is SHBG reduced?
- Obesity
- Insulin resistance
- Androgens
- Hypothyroidism
- Glucocorticoids
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Acromegaly
-
Q. What is a male escutcheon, and what is a female escutcheon?
- Pattern of pubic hair
- Male escutcheon – diamond shape
- Female escutcheon – inverted triangle shape
- Pattern of pubic hair