- Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
Support us:
- Support us by purchasing our book - Click here for more details: Volume 1- THE BEST OF NOTES IN ENDOCRINOLOGY BOOK SERIES
- Support you by Becoming a YouTube member (Click here)
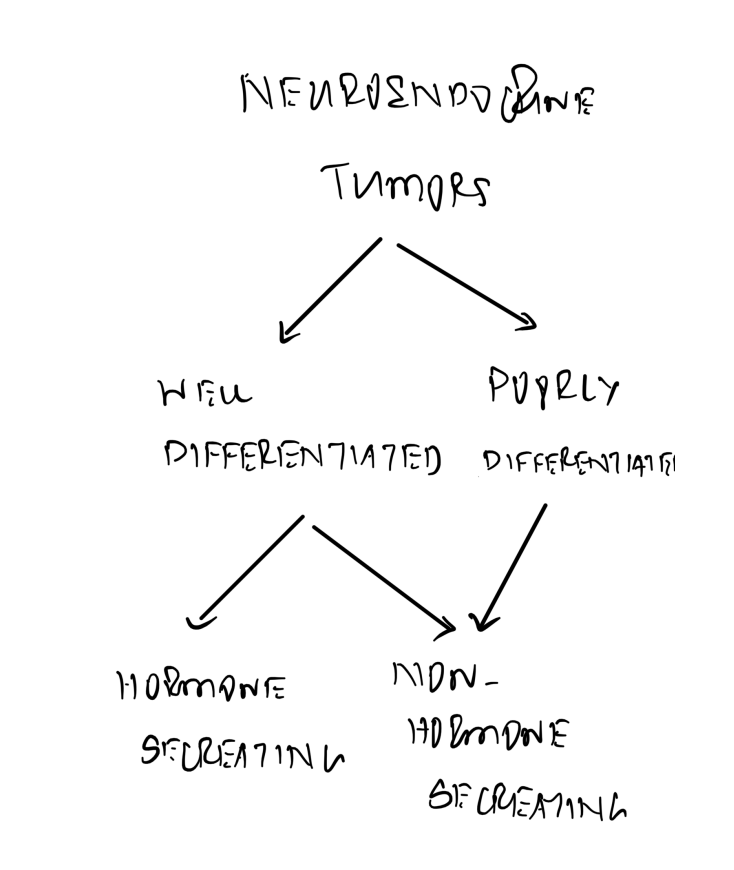
- Q. What is the broad classification of Neuroendocrine tumors (NET) ?
- Well differentiated Neuroendocrine tumors (NET)
- Poorly differentiated Neuroendocrine tumors (NET)
- Q. Which are three important non-hormonal Neuroendocrine tumor markers ?
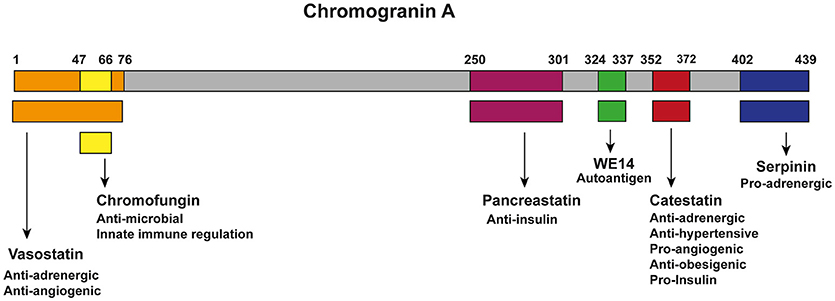
- Chromogranin A
- Pancreatic polypeptide
- Pancreastatin
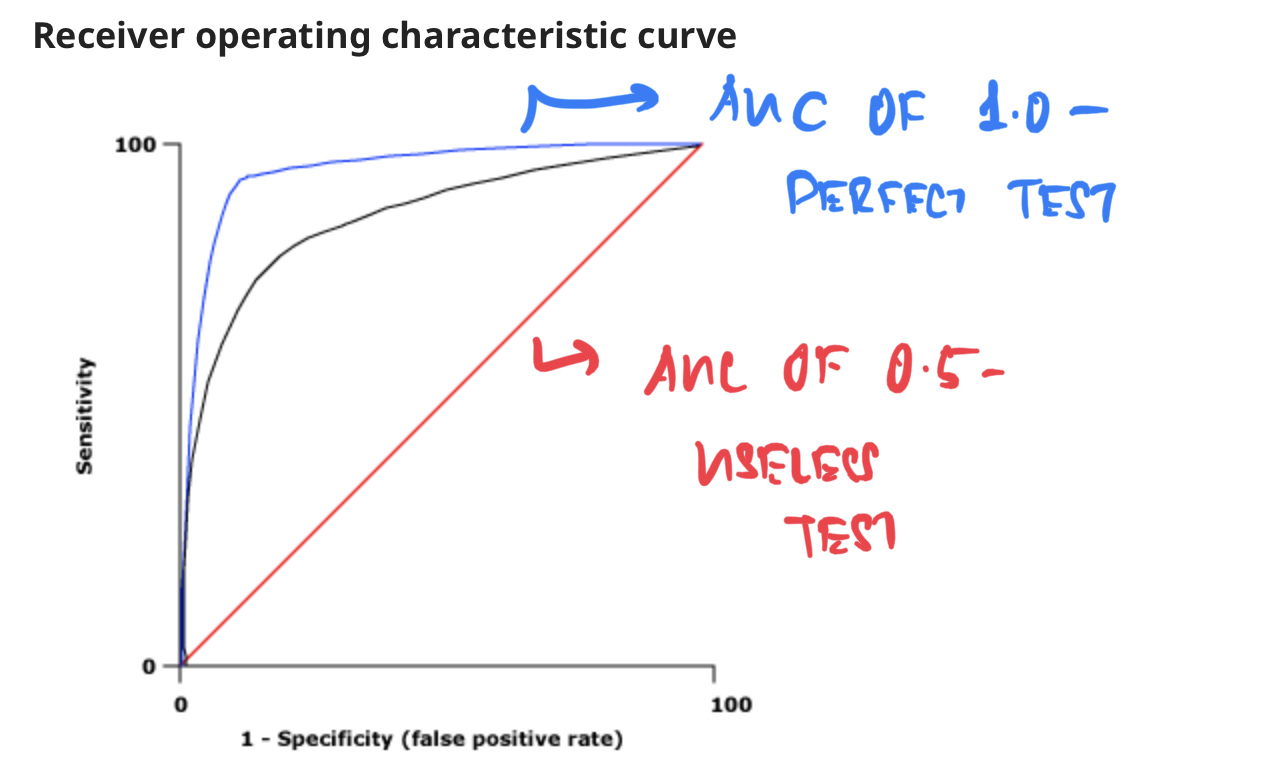
- Q. What is a ROC curve?
- ROC curve spots Sensitivity on the Y axis against 1-specificity (false positive rates) in the X axis
- Q. How is the accuracy of a test determined from the ROC curve?
- The Area under the curve (AUC) of a ROC curve represents the accuracy of a test
- The AUC of 1.0 is considered a perfect test
- Greater than 0.9 is excellent
- A AUC of 0.5 is considered a useless test -as it is 50% and likely to occur by chance
- Chromogranin A
- Q. What is the sensitivity and specificity of Chromogranin A as a tumor marker for Neuroendocrine tumors (NET) ?
- Sensitivity - 73%
- Specificity- 95%
- ROC AUC- 0.9
- Q. Chromogranin A are more sensitive for which Neuroendocrine tumors (NET) ?
- They are more sensitive to gastropancreatic NET compared to other areas like Lung
- Q. When are Chromogranin A samples taken ?
- In a fasting state
- Q. Which drug commonly produces false positive value for Chromogranin A ?
- PPI
- Q. When should Chromogranin A be measured after discontinuation of PPI ?
- Wait for 2 weeks after discontinuing PPI
- Q. Do they increase with H2 receptor antagonists also?
- Yes
- Q. Which other endocrine conditions cause elevation of Chromogranin A ?
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pheochromocytoma
- Pituitary adenoma
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Q. Enlist all the conditions in which Chromogranin A is elevated ?
- Gastroenteropancreatic NETS
- Gastrointestinal tract (carcinoid tumors)
- Pancreatic NETs (islet cell tumors*)
- Endocrine disease
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pheochromocytoma
- Pituitary tumors
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Drugs
- Proton pump inhibitors
- Histamine-2 receptor antagonists
- Inflammatory disease
- Airway obstruction in smokers
- Chronic bronchitis
- Systemic rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- Renal disorders
- Renal insufficiency/failure
- Non-gastrointestinal cancers
- Breast cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Small cell lung cancer
- Neuroblastoma
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Chronic atrophic gastritis
- Chronic hepatitis
- Colon cancer
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Liver cirrhosis
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Pancreatitis
- Cardiovascular disease
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Arterial hypertension
- Cardiac insufficiency/failure
- Essential hypertension
- Giant cell arteritis
- Gastroenteropancreatic NETS
- Q. What is another important caveat to note for patients on Somatostatin analogs for the treatment of Neuroendocrine tumors (NET) ?
- Since these agents impact the hormone activity more - the patients may have false lower values of the tumor marker
- This may not necessarily reflect the tumor mass burden
- Q. So in which cases the use of Chromogranin A is limited for a follow-up?
-
- Those on Somatostatin analogues
-
- Those with more localized disease
-
- Those with very advanced disease
-
- Q. Which is potentially a better marker than Chromogranin A ?
- Pancreastatin
- This is derived from proteolytic cleavage of Chromogranin A
- Q. Why is Pancreastatin better?
- Its level are not impacted by the use of PPI
- In small studies, the levels correlate better with tumor burden
- Q. Do current guidelines recommend the use of Chromogranin A as a tumor marker?
- Most guidelines are now moving away from recommending the same tumor marker both for diagnosis and for follow-up of patients
- It has broadly moved to become a Category III recommendation
- Q. In which patients is 5-HIAA useful as a tumor marker?
- 24-hour urinary 5-HIAA is a useful tumor marker mainly for Midgut NET
- Remember they are associated with Carcinoid syndrome
- Q. Which is the midgut NET?
- Jejunoileal
- Appendiceal
- Ascending colon
- Q. What level of gastrin is suggestive of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (gastrinoma) ?
- Fasting serum gastrin should be measured in any patient suspected of having ZES.
- ^^A serum gastrin value greater than 10 times the upper limit of normal (1000 pg/mL) in the presence of a gastric pH below 2 is diagnostic of ZES^^
- Q. Can PPI be given to patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (gastrinoma) ?
- Patients with ZES should be started on a high dose of a PPI (eg, omeprazole 40 mg twice daily, pantoprazole 80 mg twice daily).
- PPIs have been generally safe, even when used in high doses.
- Some patients require an early upward titration of these doses; however, once control of acid output has been achieved, a gradual dose reduction is usually possible
- Q. Which are other conditions causing increased gastrin levels?
-
- Chronic atrophic gastritis
-
- PPI use
-
- H. pylori infection
-
- Q. For how long should the PPI be stopped before retesting gastrin levels?
- for 10-14 days
- In such cases, patient can be shifted to a high dose of H2 blockers
- Q. Which tumor marker is suggestive of advanced or malignant Insulinoma ?
- Proinsulin levels
- They are strongly suggestive of advanced insulinoma
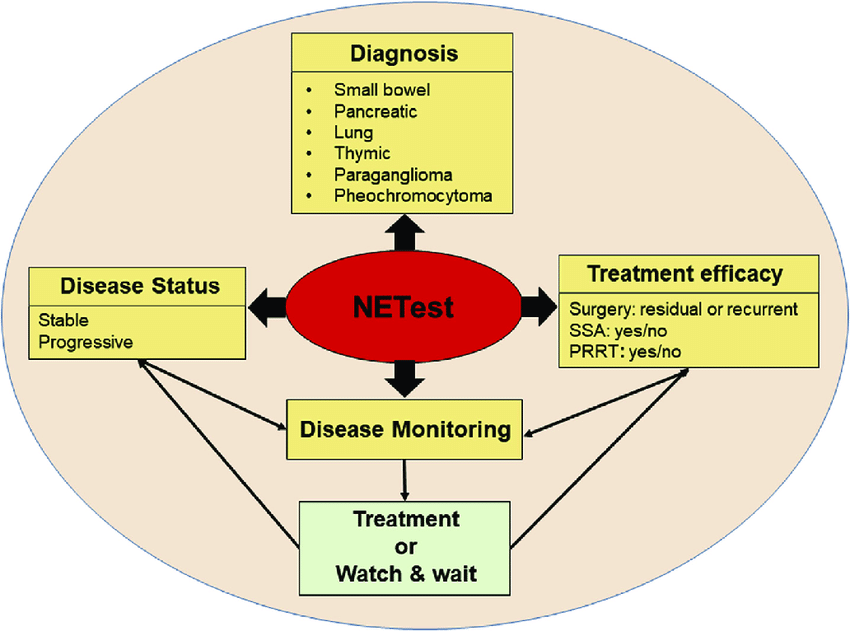
- Q. What is the NETest ?
- This is an RNA-based test
- This analyzes the tumor transcripts to look at the activity of the tumor
- This is better than Chromogranin A
- It is still under evaluation- but once we understand this better- this will become the standard of care
- This test has 95% sensitivity and 98% specificity
- It is also useful for differentiating stable disease from progressive disease