-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Q. What is the structural difference between insulin aspart and regular human insulin?
- Aspartic acid replaces proline at B28 position in Insulin Aspart
-
Q. When is the peak seen in premix insulin?
- Remember, in premix insulin, when the regular and NPH are combined, both tend to have a single common peak
- This is less of a problem with insulin analog combined with NPH
-
Q. What happens to the peak when the concentration of NPH and Regular insulin are changed?
- In 50:50 insulin – the peak occurs earlier and higher insulin concentration in the first 6 hours compared to 70:30 insulin
-
Q. Can insulin glargine and detemir be combined with other insulins?
- No
- This is because they have an acidic pH
-
Q. Give the onset, peak, and duration of various insulin?
-
Lispro/Aspart/Glulisine
- Onset- 5-15 min
- Peak- 45-75 min
- Duration - 2-4 hoursRegular human insulin
- Onset-30 min
- Peak- 2-4 hours
- Duration - 5-8 hoursNPH
- Onset- 2 hours
- Peak- 4-12 hours
- Duration - 18-28 hoursGlargine U100
- Onset- 2 hours
- Peak- None
- Duration - 22-24 hoursDegludec
- Onset- 2 hours
- Peak- None
- Duration -36-40 hours
-
-
Q. Are these timings always the same in all patients?
- No
- They are based on small doses given to normal subjects
- It may vary in the clinical situation
-
Q. Is the absorption of insulin consistent?
- No
- It may vary by 25-50% in the same person
- Variation is most with NPH and least with rapid-acting analogs
- It is also seen with glargine
-
Q. What is the relation between detemir dose and duration?
- Higher the dose of detemir, longer the duration
-
Q. What is the relation between the subcutaneous depot and variability?
- Larger the subcutaneous depot, the more the variability and lesser the absorption
- Hence Insulin pumps do very well because they have a tiny depot
-
Q. What are jet injectors?
- They produce a smaller depot and less painful
- However, they are expensive and difficult to maintain
- Hence not recommended at present
-
Q. What is the most significant advantage of a pen over a syringe and vial?
- When small doses are used- less than five units, syringe produces more errors than pen
-
Q. What is the difference between shallow injections and deep injections?
- Shallow injections produce intradermal injection – more negligible effect
- Deep injections produce intramuscular injections – a more rapid effect
-
Q. What is the microfine and ultrafine needle?
- Microfine – 27 G
- Ultrafine – 29 G
-
Q. What are the sites for injection?
- Upper arm
- Upper leg
- Abdomen
- Buttocks
-
Q. Which site has the fastest and which has the slowest absorption?
- Abdomen- fastest
- Slowest –leg and buttocks
- Arm – intermediate
-
Q. What type of insulin is given where?
- Give premeal bolus insulin at abdomen- faster absorption is more useful
- Give basal insulin at the buttocks and legs- slower absorption- prolonged duration of action
-
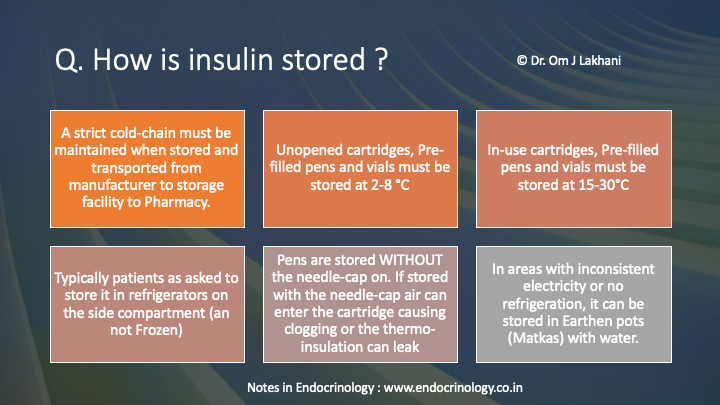
Q. How is insulin stored?
-
A strict cold-chain must be maintained when stored and transported from manufacturer to storage facility to Pharmacy
-
Unopened cartridges, Pre-filled pens and vials must be stored at 2-8 °C
-
In-use cartridges, Pre-filled pens and vials must be stored at 15-30°C
-
Typically patients as asked to store it in refrigerators on the side compartment (an not Frozen)
-
Pens are stored WITHOUT the needle-cap on. If stored with the needle-cap air can enter the cartridge causing clogging or the thermo-insulation can leak
-
In areas with inconsistent electricity or no refrigeration, it can be stored in Earthen pots (Matkas) with water.
-
-
Q. What is the shelf-life of insulin?
- Advised to look at product monograph for exact shelf-life for insulin-in-use.
- On an Average, it is 28 days.
-
Q. Whare care must be taken during the transport of insulin?
- Exposure to temperatures more than 30 degrees must be avoided
- Can be kept in handbag, flasks or special pouches for this purpose
- During air-travel it must be in the hand luggage and not in the check-in luggage
-
Q. How much potency is required for the insulin to be adequate?
- Insulin should retain a potency of at least 95% to be effective
-
Q. At an Indian room temperature of 32-37 degrees, how much potency is reduced?
- According to a study, the potency of insulin reduced by 15% in the Indian climate if insulin is NOT properly stored
- Detailed lecture on Basics of Basal insulin
Please consider donating to "Notes in Endocrinology" to keep us going. Please visit our DONATION page to know more