-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Linked notes
-
Q. Enlist the clinical consequences/correlations of Insulin resistance?
- Glucose metabolism
- Impaired glucose tolerance
- Type 2 diabetes
- Musculoskeletal
- Pseudoacromegaly
- Muscles cramps
- Muscle hypertrophy
- Cutaneous
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Skin tags
- Hirsutism
- Alopecia
- Reproductive
- Oligo-amenorrhea
- infertility and Anovulation
- Hirsutism
- Virilization
- PCOS
- Adipose tissue
- Central adiposity
- Lipodystrophy – lipoatrophy or hypertrophy
- Lipid metabolism
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Growth
- Normal, Impaired or accelerated
- Pseudoacromegaly
- Autoimmunity
- Type B insulin resistance syndrome
- Metabolic syndrome
- Glucose metabolism
-
Q. What is the reason for excess growth in Insulin resistance syndrome?
- Excess insulin has a "specificity spillover" on IGF1 receptor leading to increased growth and pseudoacromegaly like features
-
Q. Can IR be associated with hypoglycemia?
- Yes
- In those having anti-insulin antibodies
-
Q. What are the 3 characteristic histological features of Acanthosis nigricans?
- Papillomatosis
- Hyperkeratosis
- Increase melanocytes
-
Q. How does excess insulin produce ovarian hyperandrogenism?
- Ovarian theca cells have insulin and IGF1 receptors which are activated, hence theca cells produce more androgen
-
Q. Which conditions lead to growth retardation and insulin resistance?
- Leprechaunism
- Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome
-
Q. Which insulin resistance syndrome is autoimmune?
- Type B insulin resistance syndrome
-
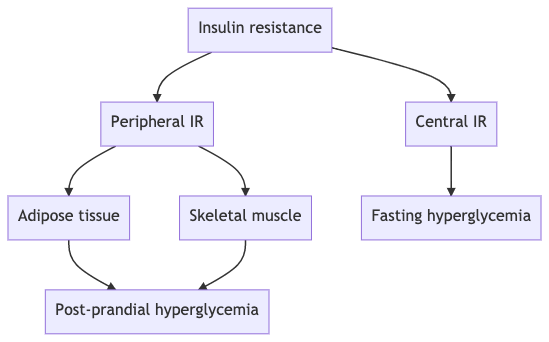
Q. What are the differential impacts of insulin resistance at various organs of the body ?
Click Here for more notes on Acanthosis Nigricans
- Source: Talk on "Assessment of Insulin Secretion and Sensitivity"
- Date: Monday, 10 May 2021
Please consider donating to "Notes in Endocrinology" to keep us going. Please visit our DONATION page to know more