-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Q. What are the indication for pancreatic and islet transplantation?
- Pancreatic transplantation
- Pancreas + kidney transplant in those undergoing kidney transplant
- Type 1 diabetes with severe recurrent ketoacidosis
- Type 1 diabetes with recurrent severe hypoglycemia
- Pancreas + kidney transplant in those undergoing kidney transplant
- Islet transplant
- It is experimental and done under a research setting
- Autografting of islet for patients undergoing pancreatic surgery is recommended
- Pancreatic transplantation
-
Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of pancreatic transplant over islet transplant?
- Pancreatic transplant leads to better insulin independence compared to islet transplantation
- However, morbidity is more with pancreatic transplant
-
Q. Describe the technique of pancreatic transplant?
- Whole pancreas with part of the duodenum containing ampulla of Vater is taken
- It is placed laterally in the pelvis
- Anastomosis is made with the iliac artery
- Drainage of the exocrine secretion is done in the intestine (previously done in the bladder)
-
Q. What is the immunosuppressive regimen used after pancreatic transplant?
- Immediate post-op - Anti T cell antibody
- Chronic – Azathioprine / Mycophenolate + Cyclosporine / Tacrolimus
-
Q. How common is acute rejection after pancreatic graft?
- Very common – 60-80%
-
Q. How is rejection detected?
- In Pancreas + Kidney transplant- the kidney is rejected first before pancreas so we see rise in creatinine
- In pancreas transplant alone– increasing amylase and blood glucose are markers of rejection
Benefits and complications associated with kidney-pancreas transplantation in diabetes mellitus
-
Q. What are the terms SPK, PAK, and PTA?
- SPK- simultaneous kidney + pancreas transplant- both from a single cadaveric do not
- PKA- Pancreas transplant after kidney transplant – pancreas from cadaveric donor, a kidney from liver or cadaver
- PTA- pancreatic transplant alone
- KTA- Kidney transplant alone
-
Q. What are the benefits of a combined SPK transplant?
- Improved survival – mainly due to the renal transplant
- Better allograft survival
- Reduced diabetic microvascular complication
- Reduced macrovascular complication
- reduced recurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Improved glycemic control
- Improve counter-regulation to hypoglycemia
- Improved quality of life
-
Q. Is patient survival better with SPK over KTA?
- Yes
- However, there are no randomized control trials and the data is mainly from uncontrolled studies
-
Q. Does SPK improve kidney allograft survival?
- Yes
- Allograft survival from cadaveric SPK is equal to liver donor KTA and better than cadaveric KTA
-
Q. Are insulin levels in blood higher after pancreatic transplant vis a vis normal person?
- Yes
- This is because insulin is released into systemic circulation instead of portal circulation which increases the insulin level
-
Q. Does pancreatic transplant worsen hypoglycemia or improve hypoglycemia?
- It may cause mild hypoglycemia due to a higher insulin level
- But the counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia improve
- This is because of glucagon
- This is one of the major advantages of the transplant
-
Q. Are complications more with SPK or KTA?
- More with SPK
-
Q. What are the major causes of pancreatic graft failure?
- Thrombosis and pancreatitis
-
Q. Where the pancreatic exocrine secretions drained?
- Earlier it was drained in the bladder- but had more complications – it used to cause normal anion gap metabolic acidosis because of loss of bicarbonate in the urine
- So now it is drained in the intestine
Islet cell transplantation
-
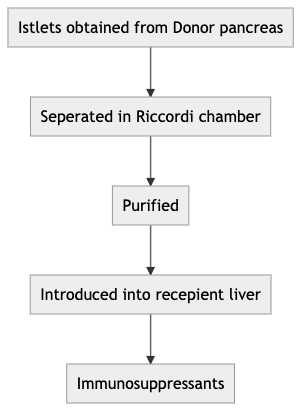
Q. Describe the steps in Islet cell transplantation? (Edmonton protocol)
-
Q. Which are the immunosuppressants used in the Edmonton protocol?
- Sirolimus
- Tacrolimus
- Daclizumab
-
Q. What was the result of the trial published with the use of the Edmonton protocol in NEJM?
- Improves glycemic stability and reduces hypoglycemia
- But does not lead to insulin independence [1]
-
Q. How are islet grafts monitored?
- PET Scan
- MRI with Magnetoencapsulation of the graft
Please consider donating to "Notes in Endocrinology" to keep us going. Please visit our DONATION page to know more
Shapiro AJ, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP, Secchi A, Brendel MD, Berney T, Brennan DC, Cagliero E. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. New England Journal of Medicine. 2006 Sep 28;355(13):1318-30. ↩︎