- Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
Support us:
- Support us by purchasing our book - Click here for more details: Volume 1- THE BEST OF NOTES IN ENDOCRINOLOGY BOOK SERIES
- Support you by Becoming a YouTube member (Click here)
- Q. Who was the first to describe HbA1c?
- Rhabar et al
- Q. What is the most appropriate Term for HbA1c?
- It is glycated hemoglobin and not glycosylated hemoglobin
- Glycosylated suggests it is an enzymatic process whereas, in reality, it is a non-enzymatic reaction
- Q. What does 1c stand for in HbA1c ?
- 1c stands for the order of hemoglobin molecules on electrophoresis
- Q. On what chain of the hemoglobin is the glucose added?
- It is added to the beta-chain of the hemoglobin
- Describe the steps to HBA1c formation?
- Glucose binds to the N terminal of valine residue on the Beta chain of HbA
- Formation of Schiff’s bases (Aldimine) non-enzymatically →
- Converts to Amadori product (Irreversible ketamine) →
- Intermediate glycosylation production →
- Cross-links- Advanced glycosylation end products
- Q. What part of the above reaction are we measuring when we measure HbA1c?
- We are measuring the irreversible ketoamine and not the Schiff’s base aldimine
- The Aldimine is transient and reflects acute glucose fluctuation
- While the Ketoamine is irreversible and represents chronic hyperglycemia
- Q. HbA1c reflects what period of glycemic control?
- It reflects truly the glycemic control of only the last 8 weeks
- Even though the idea is that it lasts the entire period of RBC which is 120 days in reality it only lasts for 8 weeks
- 50% of the HbA1c is formed in the last 1 month and that of last 3-4 months only contribute 10%
- Q. What are more glycated – The older RBCs or reticulocytes?
- The older RBCs are more glycated than reticulocytes
- Hba1c assays and methods
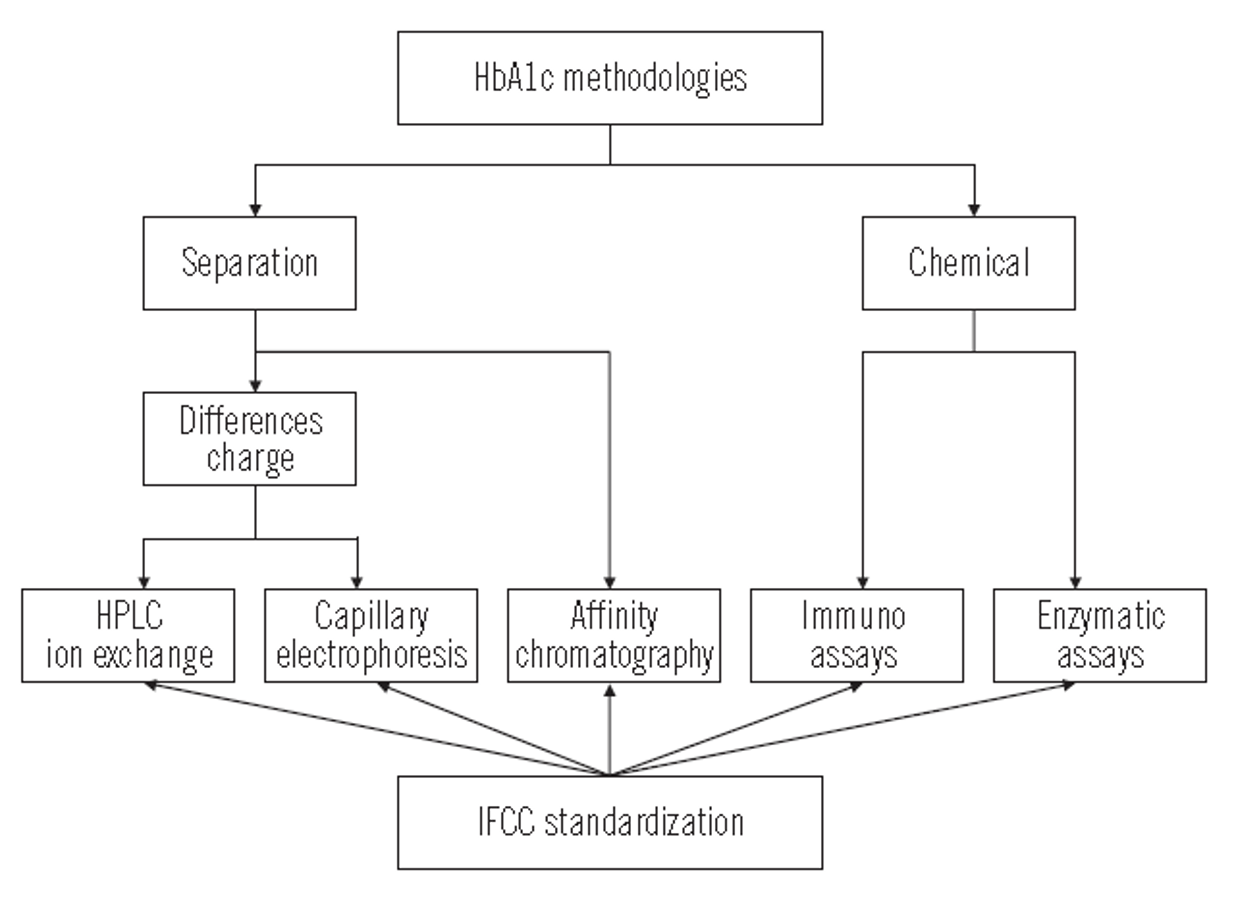
- Q. Describe the various methods for HbA1c estimation.
- Q. Which assay was used in the DCCT trial?
- It used D10 cation exchange HPLC
- To be specific- BIORAD DIAMAT using Bio-Rex 70 resin was used in DCCT and also UKPDS
- Q. What is ADAG?
- It is the study that came up with the estimated average glucose (eAG) formula for HbA1c
- Study was called "A1c Derived glucose"
- Q. What is the ADAG formula?
- eAG = 28.7 x HbA1c – 46.7
- **Standardization **
- Q. What is the difference between standardization and harmonization?
- Harmonization- calibrating the assay using an arbitrarily chosen standard
- Standardization- calibrating the assay using a standard that is of high order
- Q. What is the current standardization process for HbA1c?
- Old standardization was done by NGSP (National glycohemoglobin standardization program) which standardized using an assay that was used in DCCT
- This assay was an HPLC ion exchange electrophoresis
- It reported as % of total hemoglobin
- It was harmonization and not standardization
- The newer standardization is given by IFCC (international federation for clinical chemists)
- It is a different assay
- It reports the value as mmol/mol
- Q. How is the IFCC reference derived?
- 3 steps
- Step 1
- Hb separated from lysed RBC is cleaved using endoproteinase
- Step 2
- The glycated and non-glycated particles are separated using HPLC
- Step 3
- The glycated particles which are separated are measured using capillary electrophoresis
- Step 1
- 3 steps
- Q. How is the current reporting done?
- According to the current consensus the reporting is to be done in three formats
- IFCC – using mmol/mol value
- NGSP - % value
- eAG from ADAG formula
- Q. What is the relation between the new assay of IFCC and DCCT assay?
- The new assay gives a value that is 1.5% lower than the older assay
- Q. How is the NGSP value of % divided by the IFCC value?
- Using the formula 0.0914 * IFCC + 2.152
- Q. Using the formula what is HbA1c <7 % in IFCC terms?
- It is around 53 mmol/mol
- Q. Which anticoagulant is used while taking an HbA1c blood sample?
- EDTA
- Q. What should the CV be for HbA1c?
- Interlaboratory - CV <3%
- Intralaboratory -CV <5%
- FALSE VALUES
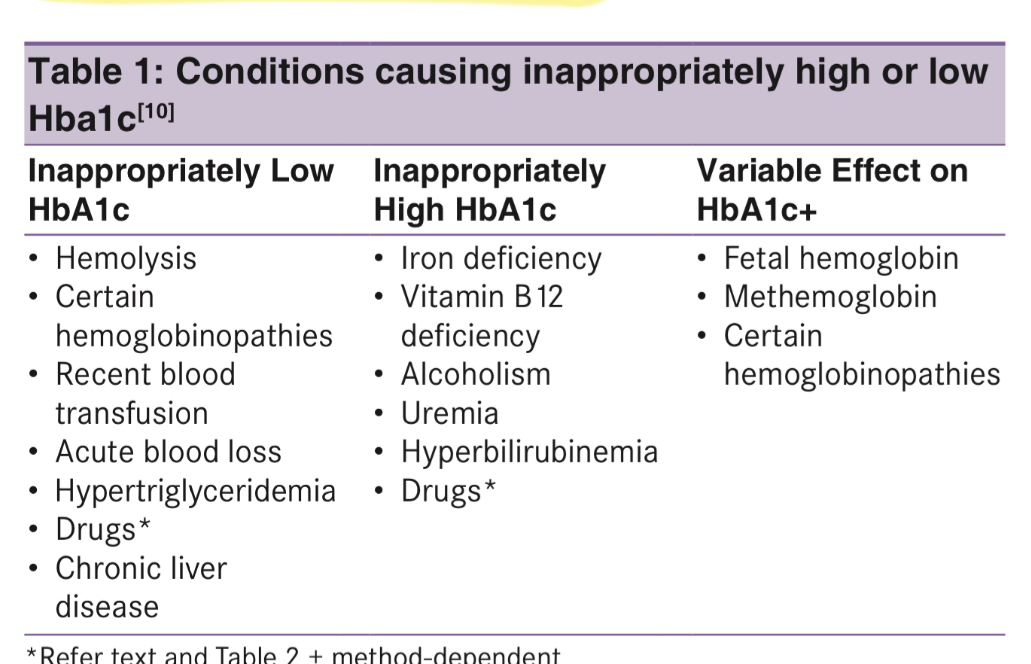
- Q. What are the common causes of false high and false low values of HbA1c?
- False High
- Iron deficiency anemia
- B12 and folic acid deficiency
- CKD (uremia)- carbamylated hemoglobin
- Asprin
- HbF and HbG
- False low
- HbS and HbC
- Hemolytic anemia
- Pregnancy
- False High
- Q. Do the Hemoglobin variants always create a problem?
- No
- The newer HPLC and Capillary electrophoresis methods tend to separate the Hb variants and hence do not interfere with the test results
- The chemical methods do not normally separate the Hb variants
- Q. What happens in CKD?
- Carbamylated Hb- false high
- Increase hemolysis and use of EPO - false low
- Q. What are the racial differences in HbA1c?
- They are uncertain
- But Africans and Hispanics- Higher HbA1c
- Asian and Caucasians- lower HbA1c
- Q. What is the relation between HBA1c and age?
- With every decade of life HBA1c increase by 0.1% or 1 mmol/mol
- Q. Why does HbA1c correlate so well with Diabetic microvascular complications
- Glucose enters the RBC via the GLUT1 channel
- here is bonds to the N-terminus of the Hemoglobin beta-chain to produce an HbA1c
- Glucose also enters the tissue in which microvascular complications are seen via GLUT1
- hence the glucose levels intracellular in these organs (kidney, retina, neurons) are similar to that in RBC
- hence HbA1c correlates well with microvascular complications
- Q. What is the Glycation gap?
- glycation gap is the difference between the measured HbA1c and the predicted HbA1c
- this article writes that in almost 30% of patients with Type 1 Diabetes - the HbA1c values do not correlate with the measured SMBG values!
- Q. Does the type of sample- arterial, venous, or capillary affect the results?
- No data regarding arterial, but generally capillary testing is similar to venous
- the difference is NOT significant
- Q. Does Point of care testing for HBA1c give inferior results?
- Not necessarily
- Q. Does HbA1c show diurnal variation ?
- No
- Q. What about seasonal variation?
- Yes
- Levels may be elevated in Winter #ClinicalPearl
- Q. How long can it be stored?
- In normal conditions, it can be stored easily
- Storage at 4 degrees is preferred for ion-exchange methods
- Long-term storage upto 10 years at -70 degrees is possible
- Q. Does drug intake interfere with the value?
- Vitamin C and Aspirin in very high doses may have an impact
- but are megadoses and not clinically relevant
- ^^#ClinicalPearl- 50% of the value of HbA1c is impacted by the glucose value in the recent months time^^ - so it is skewed mean and not exact mean of 3 months
- Q. Does Iron deficiency anemia impact the HbA1c? #ClinicalPearl
- Yes
- it increases the HbA1c because of increased RBC lifespan
- giving iron to these patients lowers the HbA1c
- Q. What happens to HbA1c in Sickle cell anemia?
- HbA1c would not be accurate in Sickle-cell anemia
- since SCA is associated with a defect in Beta-chain and HbA1c has to do with the beta-chain
- Any form of Hemoglobinopathy that leads to lower or abnormal beta-chain leads to abnormality in HbA1c values
- Q. What HbA1c value can be useful for the diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes mellitus (GDM)? #ClinicalPearl #Googlekeep
- Ball-park figure- HBA1c of >5.9% strongly correlates with GDM
- Q. Does hypothyroidism have any relation with HbA1c? #ClinicalPearl
- Some studies have shown that Subclinical hypothyroidism and Overt hypothyroidism are associated with a mild increase of HbA1c which corrects on Levothyroxine supplementation
- Q. Is HbA1c reliable in a patient with cirrhosis? #ClinicalPearl
- No
- because of several factors HbA1c is not very reliable in patients with CLD
- Q. What about CKD? #ClinicalPearl
- Some experts say
- Don't use HBA1c for diagnosis of diabetes in CKD 1-3 - can use for monitoring therapy
- Don't use HBA1c for diagnosis or treatment in patients with CKD 4/5 or ESRD
- Some experts say
- Q. Which other drugs or factors can impact HbA1c?
- Dapsone significantly reduced HbA1c and hence HbA1c should not be used in patients receiving Dapsone
- Vitamin E may also reduce HBA1c levels
- Hydroxyurea may cause aberrant HbA1c levels
- Q. Why does Dapsone reduce the HbA1c?
- By causing hemolysis
- several antiretroviral drugs like Ribavarin also impact HbA1c in a similar way
- Q. Summarize the conditions producing false high and false low HBA1c.
- Q. In which condition should you consider hemoglobinopathy and the aberrant result of HbA1c?
-
- HBA1c >15%
-
- HBA1c and SMBG do not correlate
-
- A dramatic difference in HBA1c based on change of lab or methodology
-
- Q. What is the impact of Hypertriglyceridemia on HbA1c?
- it produces false elevation of HbA1c
- Similar thing is seen with glucocorticoids use