Credit:
- Section Writer: [[Dr. Om J Lakhani]
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
Support us:
-
Support you by Becoming a YouTube member (Click here).
- Premium Membership- Download PDF version of Notes, Get ad free video and more
- Consultant Membership- Above plus Download Powerpoint presentation of the notes
-
Support us by purchasing our book - Click here for more details:
- Q. What is the definition of Non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease?
- Accumulation of fat in pancreas
- In obese individuals
- In absence of significant alcohol intake (<20 gram/day of alcohol consumption)
- Q. Give me the history of Non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease.
- The correlation between pancreatic weight and total body weight was first described by Schaefer in 1926.
- The concept of pancreatic steatosis, which refers to fat accumulation in the pancreas, was initially described in 1933 by Ogilvie, who noted that the quantity of pancreatic fat was double in obese individuals compared to non-obese individuals.
- Years later, Olsen found an increased amount of pancreatic fat in direct relation to age after an autopsy study of 394 cases.
- Subsequently, Stamm reached the same conclusion, finding a significant relationship between pancreatic steatosis and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and atherosclerosis when the pancreatic fat content was greater than 25%.
- Q. What are the two types of fat deposition in the pancreas ?
-
- Replacement of dead acinar cells with adipocytes
-
- Fat infilteration and accumulation in the pancreas
- Basically the fat accumulation could be:
-
- Intra-lobular- inbetween the cells of the pancreas
-
- Intra-acinar- within the cells of the pancreas
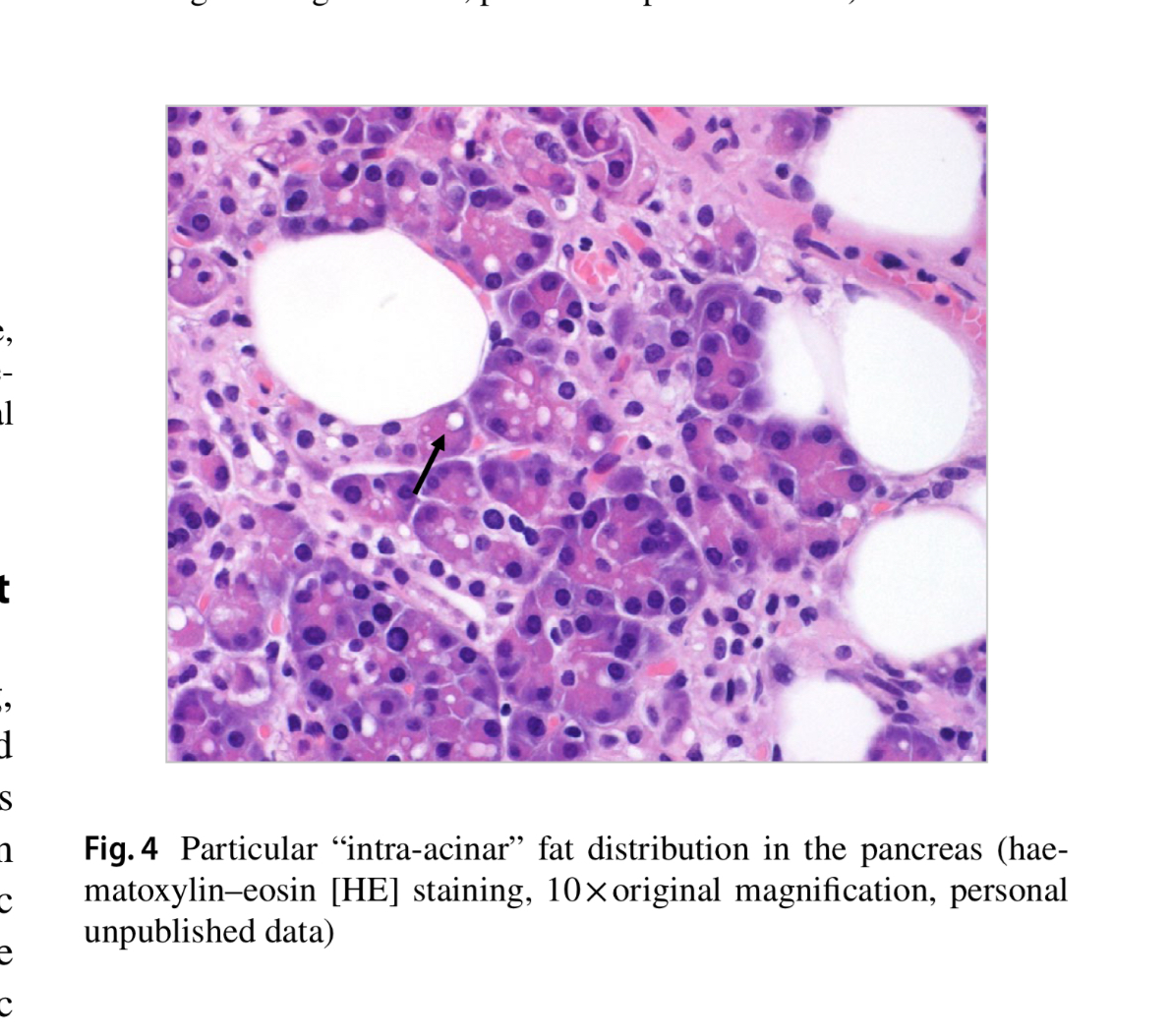
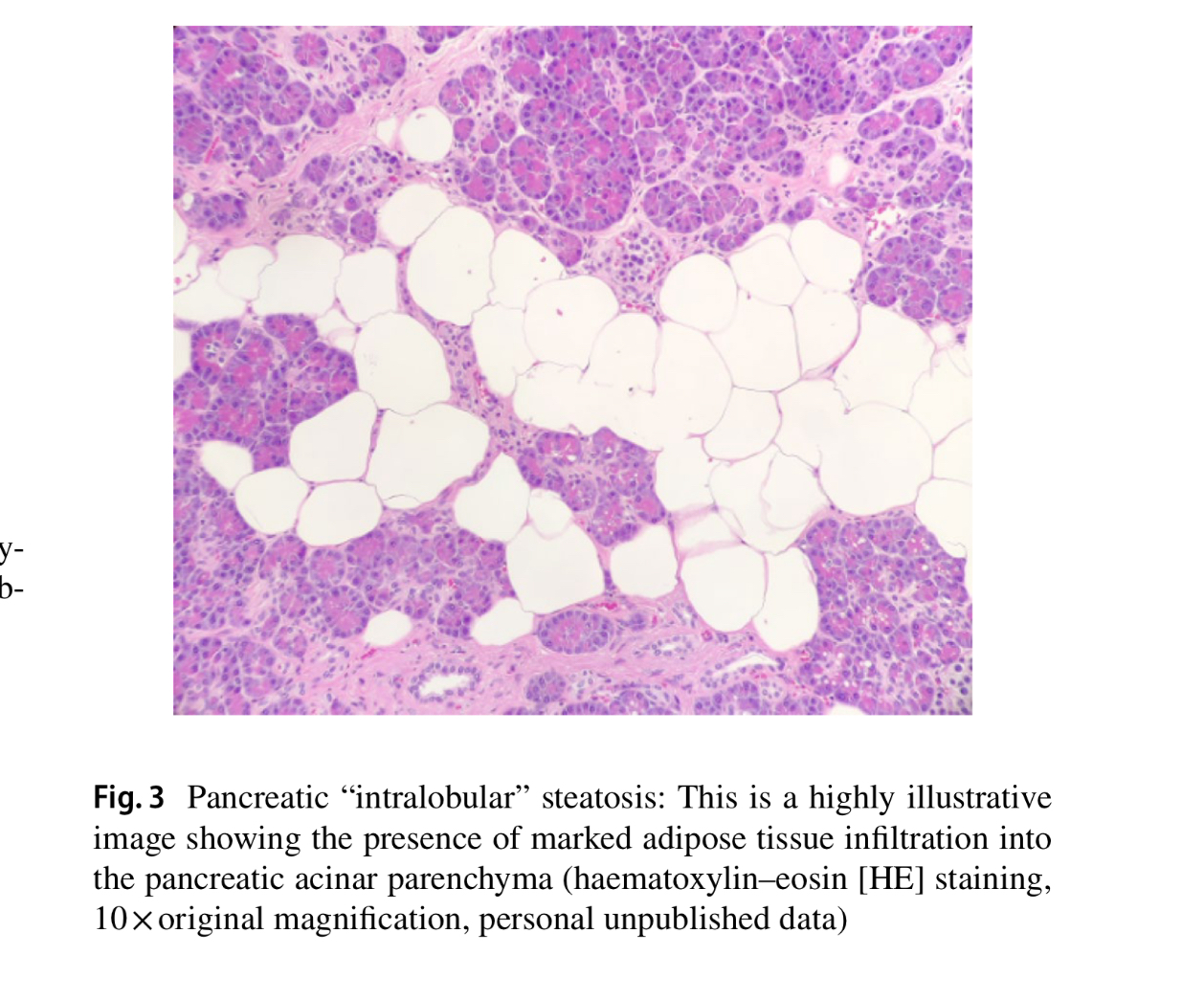
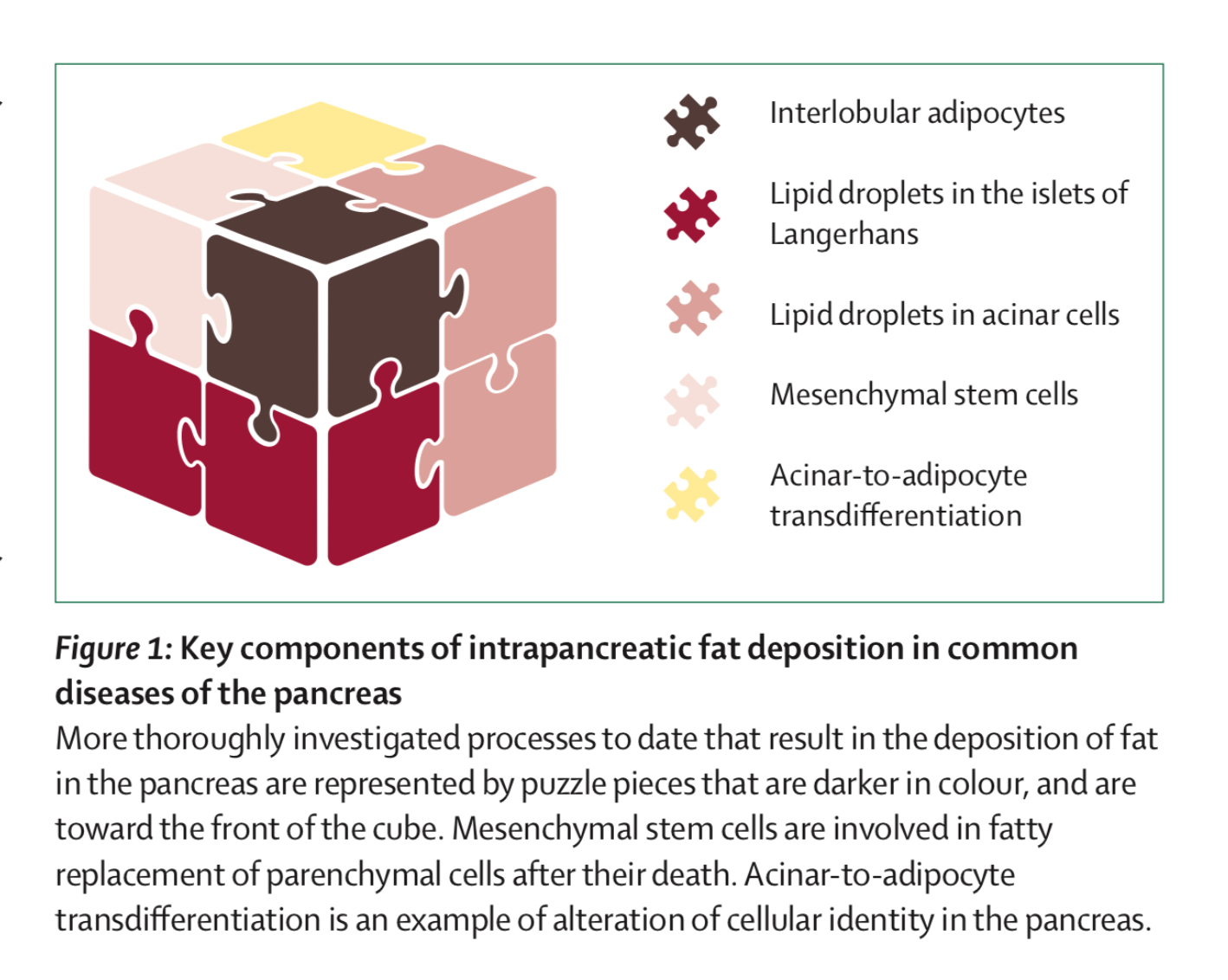
-
-
- Q. What is the correlation between NASH/NAFLD and Non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease ?
-
- Fifty percent patient with NASH also has NAFPD
-
- Presence of NAPFD is strongly linked with advanced fibrosis in NASH
-
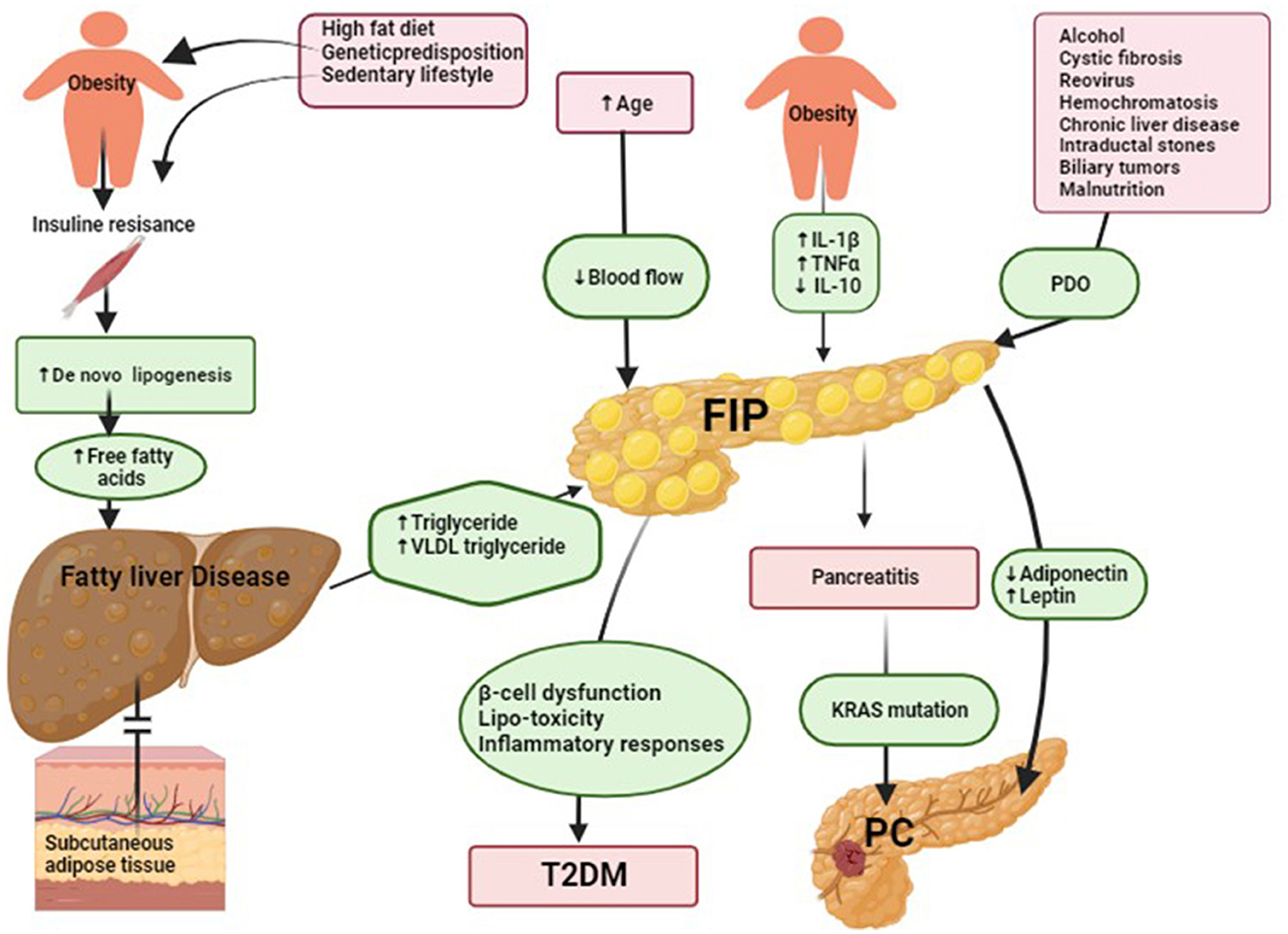
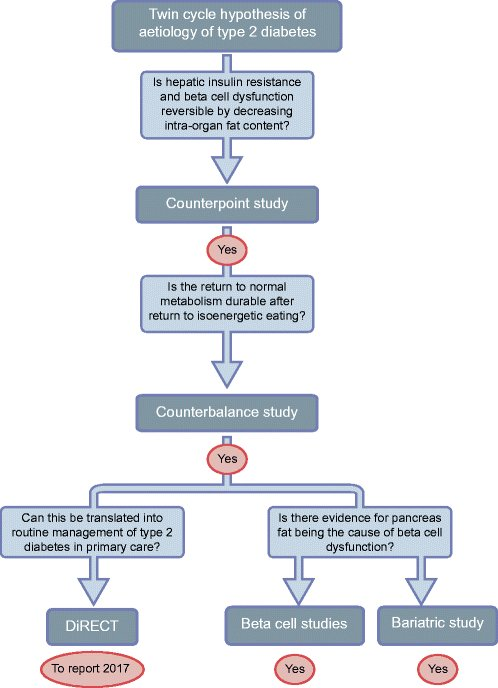
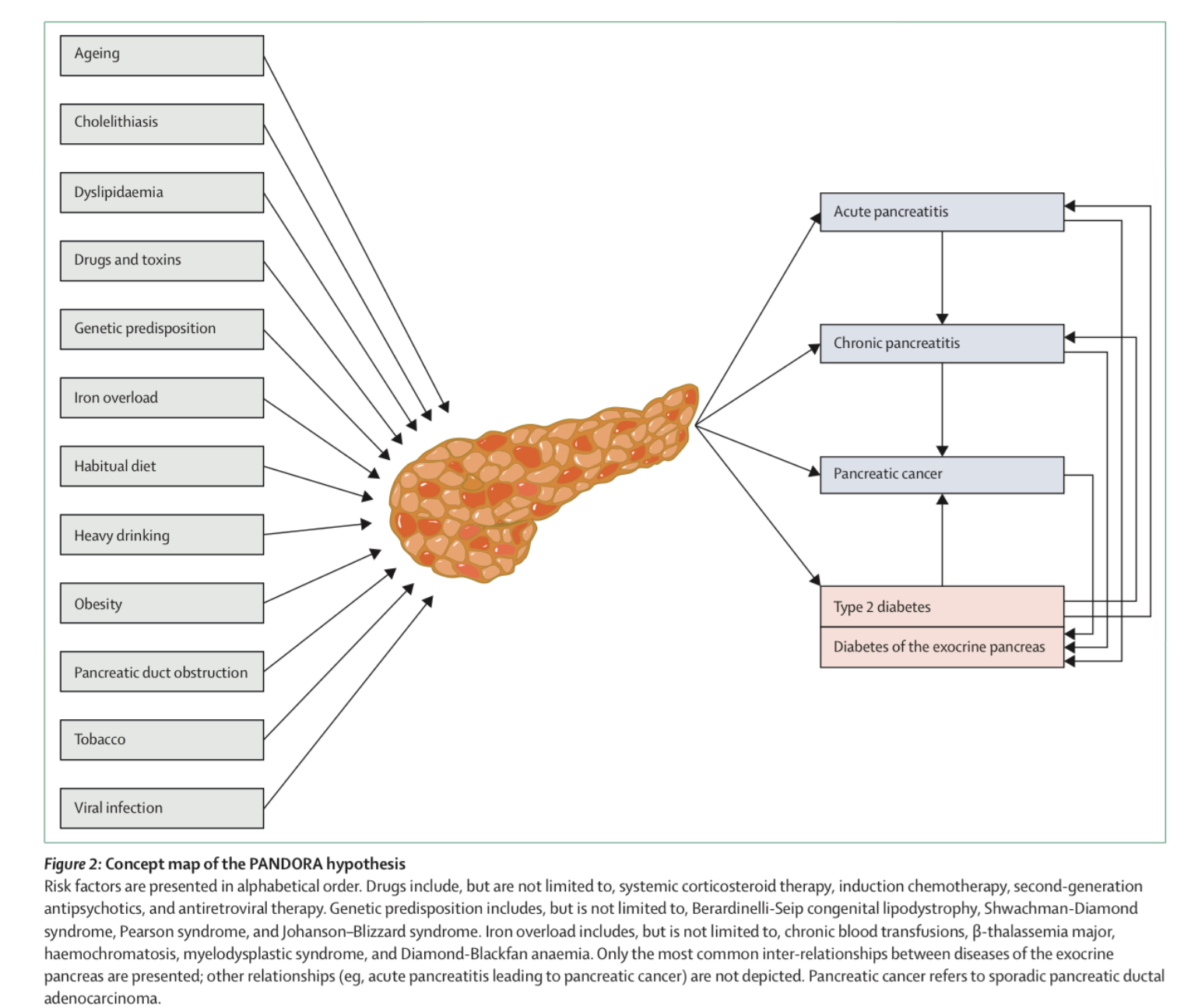
- Q. What is the PANDORA hypothesis ?
- This is given by Prof Maxim Petrov, the summary is in the picture below
- Ref: Petrov MS. Fatty change of the pancreas: the Pandora's box of pancreatology. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2023 Jul 1;8(7):671-82.
- Diagnosis
- Q. What is the gold standard for diagnosis of Non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease ?
- Biopsy
- Fat content for >6.2% is diagnostic
- Q. Can it be diagnosed using USG
- Transabdominal ultrasound- if you visualize the pancreas- fatty pancreas is more hyperechoic compared to kidney and liver
- However, even fibrosis can appear hyperechoic
- Also difficult to visualize pancreas in obese individuals
- EUS can be used for better visualization
- There is no basic cut-off for the same
- Q. What about CT Scan ?
- So fat in pancreas has less density
- Cut-off of 36 HU is proposed- less than that suggest fatty pancreas
- Q. Which is the imaging technique of choice for fatty pancreas ?
- MRI
- Q. What different types of MRI sequences are useful for diagnosis of Fatty pancreas ?
-
- Chemical shift MRI
-
- MR spectroscopy
-
- IDEAL
-
- MR-PDFF
-
- MR elastography
-
- Q. What is IDEAL ?
- IDEAL stands for Iterative Decomposition of Water and Fat with Echo Asymmetry and Least squares estimation.
- It is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique developed for evaluating pancreatic fat content.
- IDEAL offers accuracy and less signal contamination in measuring pancreatic fat.
- This technique has been validated in animal models.
- It is expected to replace MR spectroscopy (MRS) as the gold standard for quantifying pancreatic fat accumulation.
- IDEAL combines spatial anatomical and quantitative data, benefiting from MRI's noninvasiveness, safety, and high sensitivity
- Q. What is MR-PDFF ?
- MR-PDFF stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Proton Density Fat Fraction.
- It is an imaging technique used to quantify the amount of fat in tissues, including the liver and pancreas.
- MR-PDFF utilizes the differences in the magnetic resonance properties of water and fat to accurately measure fat content.
- It provides a noninvasive, accurate, and reproducible method for assessing and monitoring fat levels in organs.
- The technique is particularly useful in diagnosing and managing conditions related to fat accumulation, such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease (NAFPD).
- MR-PDFF can help in the evaluation of the efficacy of treatments aimed at reducing organ fat content.
- Unlike biopsy, MR-PDFF is a safe and noninvasive method, making it suitable for repeated measurements over time.
- Q. What is the role of MR-Elastography in fatty pancreas ?
- MR-Elastography (MRE) is an advanced MRI technique that measures the stiffness of tissues, including the pancreas.
- In the context of a fatty pancreas, MRE can help in identifying and quantifying the degree of fibrosis, which often accompanies fat accumulation.
- Since pancreatic fibrosis can indicate chronic pancreatitis or an increased risk for developing pancreatic diseases, MRE provides valuable diagnostic information beyond just fat content.
- MRE's ability to assess tissue stiffness noninvasively offers a significant advantage over traditional invasive biopsy methods.
- This technique can be useful in monitoring the progression of pancreatic disease and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing fat and fibrosis in the pancreas.
- By providing detailed information on the mechanical properties of pancreatic tissue, MRE contributes to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of fatty pancreas and related conditions.
- Overall, MR-Elastography plays a critical role in the comprehensive assessment of pancreatic health, aiding in the diagnosis, management, and monitoring of patients with fatty pancreas and associated diseases.
- Q. What is the role of MR-Elastography in fatty pancreas?
- MR-Elastography (MRE) is an advanced MRI technique that measures the stiffness of tissues, including the pancreas.
- In the context of a fatty pancreas, MRE can help in identifying and quantifying the degree of fibrosis, which often accompanies fat accumulation.
- Since pancreatic fibrosis can indicate chronic pancreatitis or an increased risk for developing pancreatic diseases, MRE provides valuable diagnostic information beyond just fat content.
- MRE's ability to assess tissue stiffness noninvasively offers a significant advantage over traditional invasive biopsy methods.
- This technique can be useful in monitoring the progression of pancreatic disease and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing fat and fibrosis in the pancreas.
- By providing detailed information on the mechanical properties of pancreatic tissue, MRE contributes to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of fatty pancreas and related conditions.
- Overall, MR-Elastography plays a critical role in the comprehensive assessment of pancreatic health, aiding in the diagnosis, management, and monitoring of patients with fatty pancreas and associated diseases.
- Clinical consequences
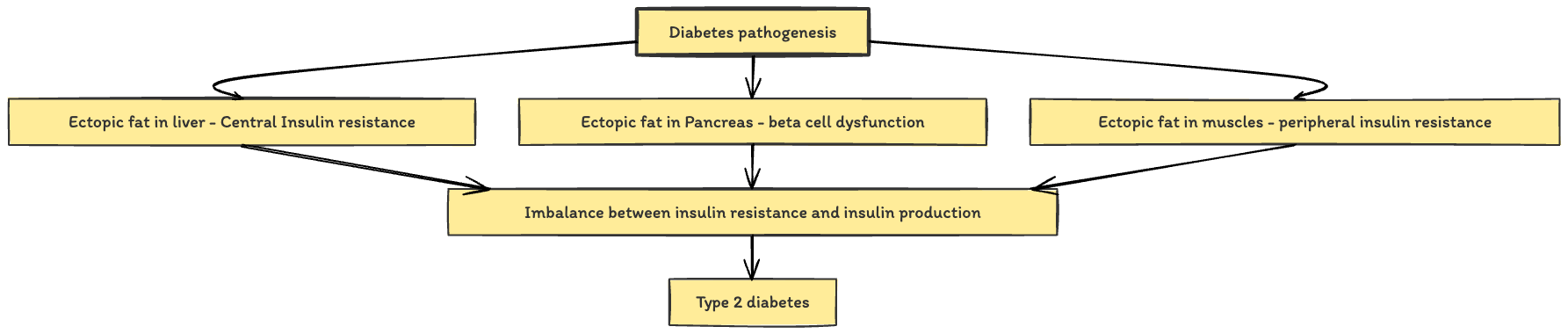
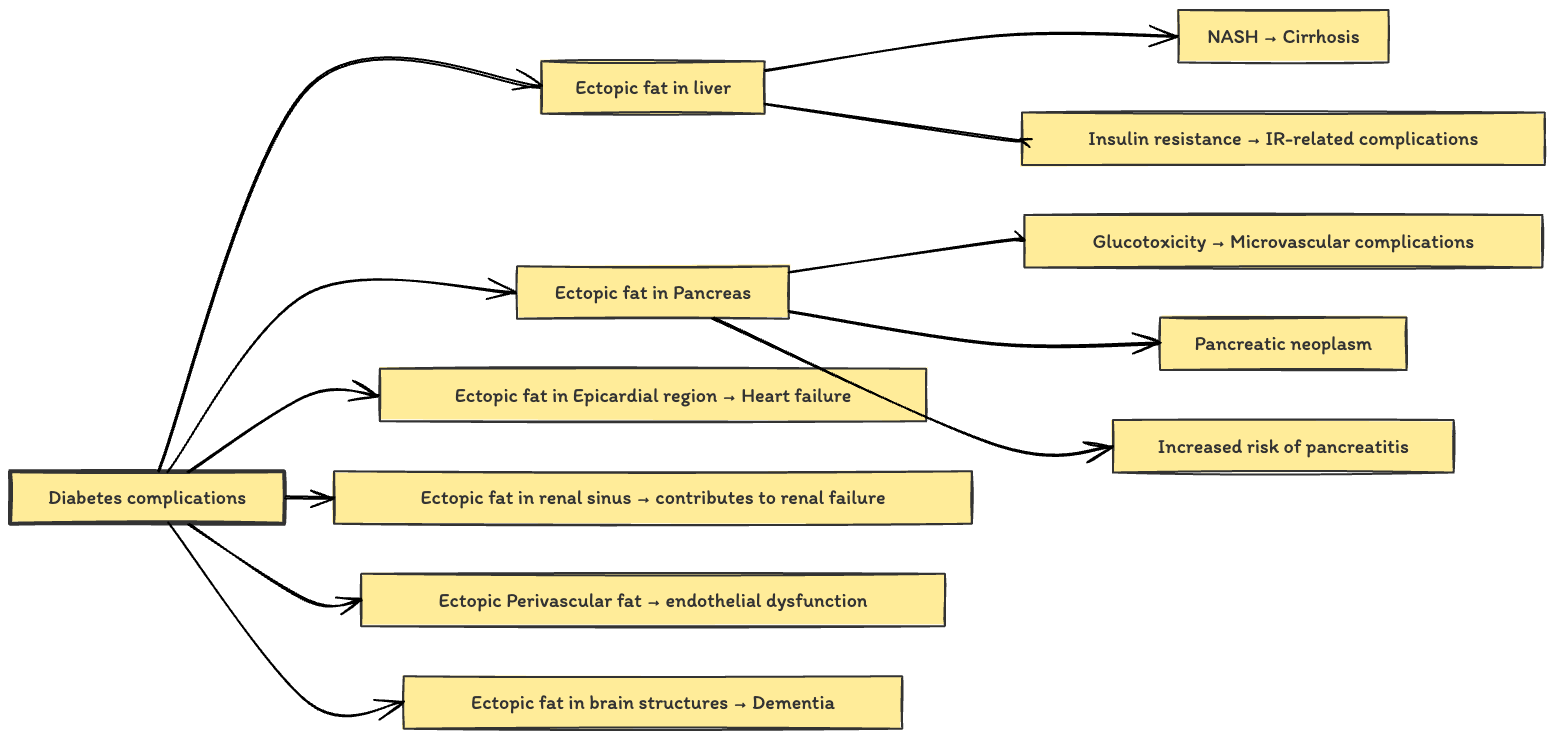
- Q. Summarize the role of Ectopic fat in clinical presentation and complications of type 2 diabetes ?
- Layer 1
- Layer 2
- Layer 1
- Q. Is there any Indian data to show the relationship between the ectopic fat and insulin resistance ?
- Study by Garg et al concludes : "In individuals suffering from T2D and MetS, IR shows a trend towards positive and borderline negative correlation with liver fat and Subcutaneous adipose tissue fat masses respectively"
- Garg UK, Mathur N, Sahlot R, Tiwari P, Sharma B, Saxena A, Jainaw RK, Agarwal L, Gupta S, Mathur SK. Abdominal fat depots and their association with insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2023 Dec 8;18(12):e0295492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295492. PMID: 38064530; PMCID: PMC10707599.

- Study by Garg et al concludes : "In individuals suffering from T2D and MetS, IR shows a trend towards positive and borderline negative correlation with liver fat and Subcutaneous adipose tissue fat masses respectively"
- Q. Summarize the clinical aspects of Non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease with a picture
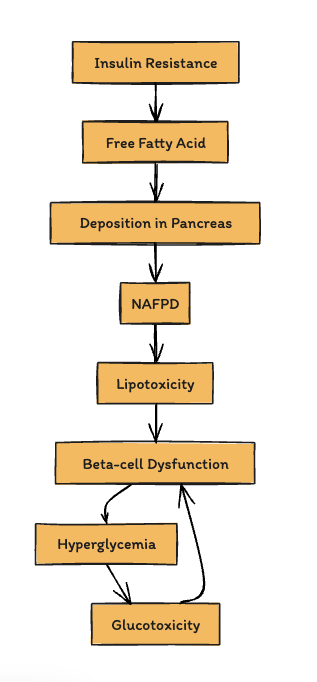
- Q. Does Non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease lead to Beta-cell dysfunction ?
- Yes
- This is what basically happens:
- Q. Does it lead to exocrine dysfunction ?
- Some studies have shown that NAFPD also leads to exocrine dysfunction in both adults and children
- In fact it is thought to be an important cause of pancreatic exocrine dysfunction in pediatric age group
- Q. What are the other association with NAFPD as far as pancreas is concerned ?
-
- Increase risk of Pancreatic cancer
-
- Increased risk of acute pancreatititis
-
- Q. What is the importance of this disease as far as Diabetes remission is concerned ?
- A lot of Roy Taylor's work has shown that weight loss leads to Diabetes remission
- One of the reason proposed for the same is that weight loss reduces pancreatic and liver fat (The Twin cycle hypothesis)
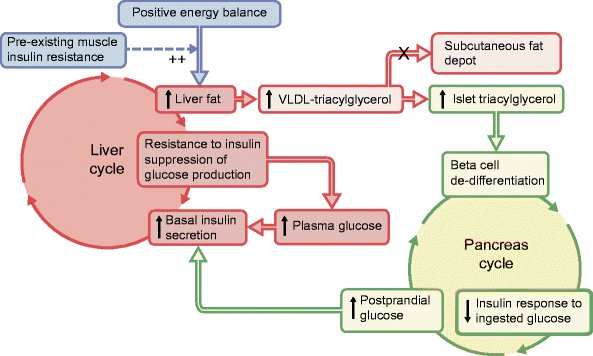
- Q. Can you summarize the evidence of on pancreatic fat and beta-cell dysfunction
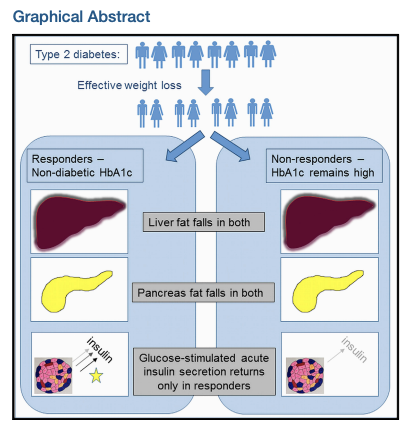
- Q. Does reversal of pancreatic fat lead to improvement in beta-cell function in all patients ?
- No
- It depends on the ability of beta-cell ability to recover
- It may not happen in all patients
- " This study demonstrates that β cell ability to recover long-term function persists after diagnosis, changing the previous paradigm of irreversible loss of β cell function in type 2 diabetes"
- Treatment
- Q. What is the first line treatment for NAFPD ?
- The first line treatment is weight loss just like NAFLD
- Q. Does Aerobic exercise help ?
- Yes
- A study published in "Diabetes Metab Res Rev" in May 2022 explored the effects of six months of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise on pancreatic fat content and its impact on β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes. The study found that aerobic training significantly reduced pancreatic fat content, which was an independent protective factor for improving β-cell function and HbA1c levels
- Q. Can SGLT2i be helpful in reducing the pancreatic fat ?
- SGLT2 inhibitors, specifically empagliflozin, have shown promise in reducing ectopic fat stores, including pancreatic fat, in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- However this is an area of debate and under research
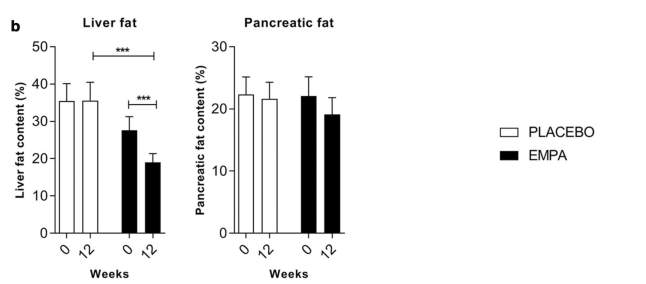
- A study known as EMPACEF investigated the effects of empagliflozin over 12 weeks on ectopic fat stores and myocardial energetics in Mice model and humans.
- This randomized, double-blind trial included subjects with type 2 diabetes who were either treated with empagliflozin or a placebo.
- The study measured changes in ectopic fat stores, including pancreatic fat, using magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy.
- "Per-protocol analysis confirmed the results obtained in ITT analysis with no significant reduction of EAT, myocardial, or pancreatic fat, but a significant reduction of visceral fat"
- However, a study done from India has shown reduction of pancreatic fat with the use of Dapagliflozin
- "Dapagliflozin, after 120 days of use, reduced pancreatic and liver fat and increased insulin sensitivity in Asian Indian patients with T2DM."
- Q. Any study showing GLP1 receptor agonist reducing pancreatic fat ?
- Study by Kuchay et al from India has shown that GLP-1 receptor agonist has little on no impact on reduction of pancreatic fat content
- "Absolute changes in PFC (-1.4% [-3.2, 0.3]; p = 0.106) and LSM (-1.31 kPa [-2.99, 0.37]; p = 0.123) were not significant when comparing the two groups"
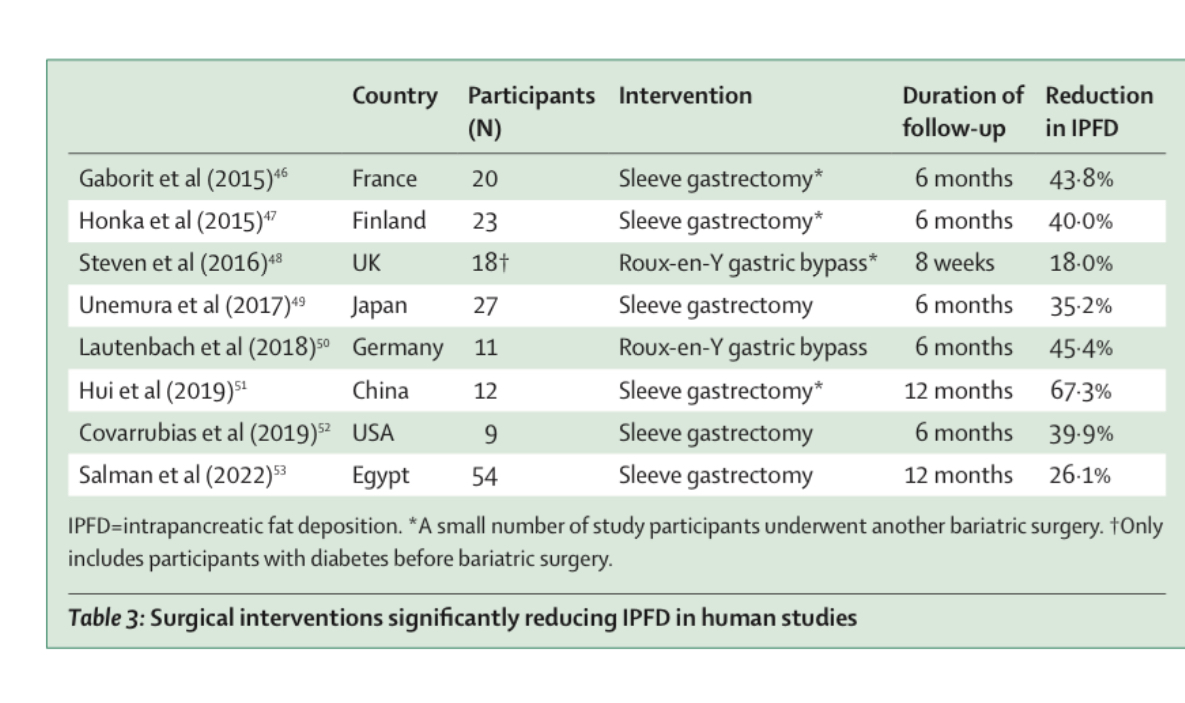
- Q. Does Obesity surgery reduce intrapancreatic fat deposition ?
- Yes
- Several studies have shown this impact
References:
- Zhang CL, Wang JJ, Li JN, Yang Y. Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease: Anemerging clinical challenge. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(23): 6624-6638
- Li M, Zheng Q, Miller JD, Zuo P, Yuan X, Feng J, Liu C, Bao S, Lou Q. Aerobic training reduces pancreatic fat content and improves β-cell function: A randomized controlled trial using IDEAL-IQ magnetic resonance imaging. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2022 May;38(4):e3516. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3516. Epub 2022 Feb 2. PMID: 34963031.
- Gaborit B, Ancel P, Abdullah AE, Maurice F, Abdesselam I, Calen A, Soghomonian A, Houssays M, Varlet I, Eisinger M, Lasbleiz A. Effect of empagliflozin on ectopic fat stores and myocardial energetics in type 2 diabetes: the EMPACEF study. Cardiovascular Diabetology. 2021 Dec;20:1-4
- Ghosh A, Dutta K, Bhatt SP, Gupta R, Tyagi K, Ansari IA, Venugopal VK, Mahajan H, Pandey RM, Pandey S, Misra A. Dapagliflozin Improves Body Fat Patterning, and Hepatic and Pancreatic Fat in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in North India. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 May 17;107(6):e2267-e2275. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac138. PMID: 35263436.
- Kuchay MS, Krishan S, Mishra SK, Choudhary NS, Singh MK, Wasir JS, Kaur P, Gill HK, Bano T, Farooqui KJ, Mithal A. Effect of dulaglutide on liver fat in patients with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD: randomised controlled trial (D-LIFT trial). Diabetologia. 2020 Nov;63:2434-45.