Support us:
- Support you by Becoming a YouTube member (Click here).
- Premium Membership- Download PDF version of Notes, Get ad free video and more
- Consultant Membership- Above plus Download Powerpoint presentation of the notes and get access to EndoAI for Free
- Support us by purchasing our book - Click here for more details:
- Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
Also see Vitamin D beyond bones- was it all just a hype- Balanced view of current status
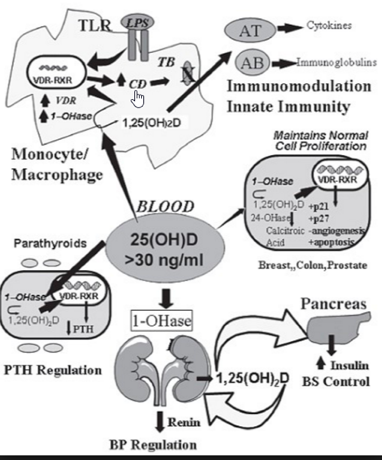
- Q. Enlist the Non-Calciotropic actions of Vitamin D
- Action on the skin is not known, but VDDR type 2 have had alopecia totalis
- Hypertension- Vitamin D reduces renin levels
- CV risk :Vitamin D Deficiency increase risk of thrombosis
- Glucose metabolism: 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D has a favorable effect on glucose metabolism
- Cancer: Vitamin D reduces cell proliferation and increases cell differentiation
- Immune action
- Muscles - Vitamin D Deficiency produces proximal muscle weakness an increased risk of falls
- Neuro-psychiatric functions
- 
- Q. Summarize the cardiovascular and metabolic actions of vitamin D?
- Heart
- Increase cardiac contractility
- Reduces cardiac remodeling
- Blood vessels
- Increase release of endothelial Nitrous oxide
- Reduce thrombogeneticity
- Promotes vascular repair via increase vascular smooth muscle differentiation
- Modulation of vascular calcification
- Reduces local inflammation
- Kidney
- Reduces Renin reduces BP
- Reduces proteinuria
- Lipid
- Reduces Apo AI
- Pancreas
- Increases insulin release
- Reduces insulin resistance
- 
- Q. Does current evidence suggest the replacement of vitamin D to reduce CV risk?
- No
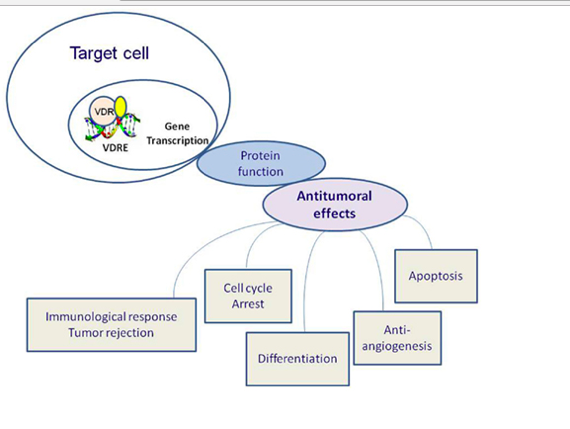
- Q. Summarize the anticancer actions of vitamin D?
- Reduces Cell differentiation
- Cell cycle arrest
- Apoptosis
- Anti-angiogenesis
- Immune rejection of the tumor
- 
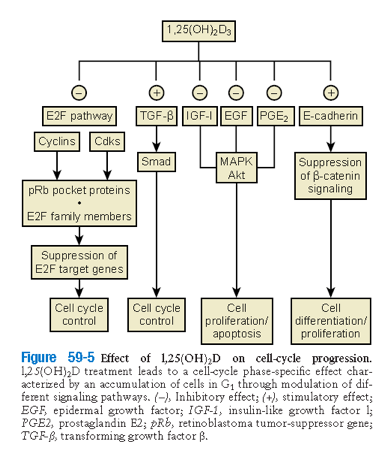
- Q. Summarize the action of vitamin D on the cell growth pathway?
- Vitamin D Increases
- TGF beta which controls cells growth cycle
- E- Cadherin- induces cell differentiation
- 2. Vitamin D reduces
- E2F pathway – reduce cell cycle
- Growth factors- IGF1, EGF, PGE2 – reduce cell growth
- 
- Q., vitamin D polymorphism, is associated with which cancers?
- Breast
- Prostate
- Thyroid
- Melanoma
- Colorectal
- Q. Benefit of vitamin D has been demonstrated in which cancers?
- Breast
- Prostate
- Melanoma
- Colon
- Value <20 ng/ml- increased risk of breast cancer and melanoma
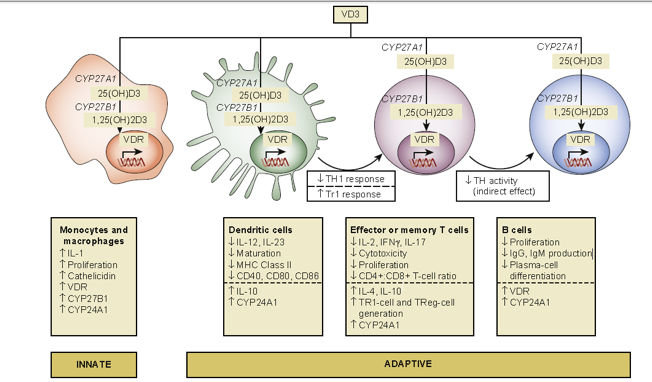
- Q. Summarize the actions of vitamin D on the immune system?
- Enhances innate immunity
- Modulates Adaptive immunity
- Reduces Th1 response
- Increases Th2 response
- Reduces production of IgG by B cells
- Increases Treg cell function
- Q. vitamin D has been tried in which immune-mediated disorders?
- Multiple sclerosis
- Asthma
- Type 1 diabetes
- 
- Q. Summarize the actions of vitamin D on the muscle?
- Vitamin D may have non-genomic actions on muscles
- Some of the action on muscle may be mediated by vitamin D binding protein
- Vitamin D is proposed to activate cell surface receptors on muscles which can trigger the MAPKinase pathway – leading the increase myogenesis
- Q. What is the evidence of the direct impact of vitamin D on muscles?
- 1. VDR knock out mice have muscle atrophy
- 2. patients with vitamin D dependent rickets- defect in vitamin D receptor have myopathy
- Recent experiment has shown that treatment with 25 hydroxyvitamin D increases the VDR mRNA expression in C2C12 myoblasts
- In recent experiments – treatment with vitamin D increased the number of vitamin D receptor in the muscle by 29%
- Q. What are the evidence of the indirect impact of vitamin D in muscles?
- 1. Some studies have shown the clear absence of vitamin D receptors in muscles and have challenged this notion
- 2. not all patients with low vitamin D have myopathy
- 3. some experiments have shown knock out of intestinal vitamin D receptor leads to muscle atrophy
- A high dose of calcium can reverse features of osteomalacic myopathy in some patients
- High PTH can lead to myopathy and poor contractility
- Q. What does RCT for vitamin D supplementation say?
- There is a meta-analysis that says that if the starting vitamin D is <10 ng/ml- there is an improvement in the muscle function with treatment
- However, If the starting vitamin D > 10 ng/ml, there is a slight improvement in muscle function with treatment
- Another RCT explored the role of vitamin D in preventing falls
- They grouped the studies according to a dose of vitamin D used
- They found that studies that used a low dose of vitamin D – 200 IU found no benefit in preventing falls
- Studies showing a higher dose of vitamin D of 700-100 IU/day found risk reduction in falls with vitamin D supplementation
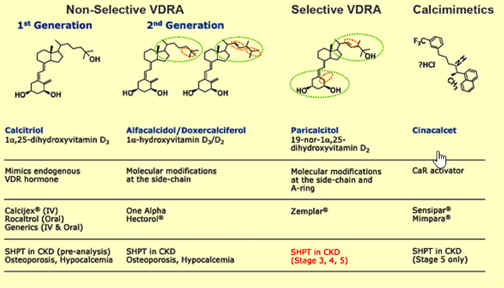
Vitamin D analogs
-
Q. Summarize the use of various vitamin D analogs?
- Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT)- 22-oxacalcitriol
- Renal osteodystrophy – PARACALCITOL
- Psoriasis- topical TACALCITOL, CALCIPOTRIOL
- Prostate hyperplasia- ELOCALCITIOL
- Immune system
- Cancer
- Osteoporosis
- Reducing fall- ELDECALCITOL -
Q. Summarize the Vitamin D analogs as pe generation?
- 1st Generation- Calcitriol
- 2nd generation - Alphacalcidiol, Doxecalciferol
- 3rd Gen – Paracalcitol and Cinacalcet
-
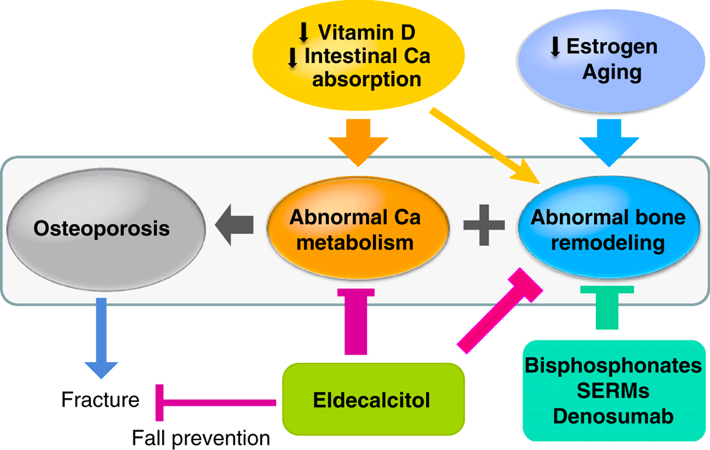
Q. How does Eldecalcitol benefit for osteoporosis?
- Reduces fracture
- Reduces the abnormal calcium metabolism
Vitamin D and Diabetes
-
Q. Where does the evidence of vitamin D action in type 1 diabetes come from?
- “Mainly indirect evidence.”
- Mainly from observation studies which have shown that vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased risk of diabetes
- Case-control studies have shown that vitamin D reduces the risk of type 1 diabetes by 30%
- However, there are no RCT for the use of vitamin D in type 1 diabetes
- Genetic polymorphism in vitamin D has been associated with diabetes -
Q. How does vitamin D reduce the risk of type 1 diabetes? (what is the pathogenesis)
- Immune modulation
- Increase insulin secretion
- Reduce beta cell apoptosis -
Q. How does vitamin D reduce beta-cell apoptosis?
- Vitamin D activates- Nf- kb pathway, which increases beta-cell survival -
Q. What kind of immune modulation is seen with vitamin D, which is beneficial for type 1 diabetes?
- Reduces Th1
- Increases Th2
- Reduces production of IgG by B cells
- Increases Treg cell function
- Reduce damaging cytokine production
- Vitamin D and innate and adaptive immunity.-
Q. What is the relation between obesity and Vitamin D Deficiency?
- “Definitely relation but not cause-effect.”
- Vitamin D is low in obese people
- This has been proven in numerous studies
- However, a causal relation is not proven-
Q. What is the relation of Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes?
- Again, in case-control studies – diabetes is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes
- However, interventional trials except for a few have largely been negative
-
Q. Are VDR (Vitamin D receptors)present in beta cells of the pancreas?
- Yes
-
Q. Which studies have shown a link between type 2 diabetes and vitamin D?
- NHANES III study
- Nurses health study
-
Q. Summarize how vitamin D benefits type 2 diabetes?
- Increase insulin secretion
- Reduce insulin resistance
- Reduce beta-cell apoptosis- NFkb pathway
-
Q. What is the action of vitamin D on insulin secretion?
- Vitamin D enhances insulin secretion by pancreatic beta cells
- Direct action enhances Insulin gene expression
- Indirect
- increase intracellular calcium, which aid In insulin release
- Increase calbindin
-
Q. What is the relation between calbindin and insulin?
- Calbindin 28K is known to increase insulin secretion
-
Q. What is the action of insulin on insulin sensitivity?
- Vitamin D reduces insulin sensitivity
- Direct action
- Increase insulin – receptor gene expression
- Increase activity of PPAR- delta and PPAR- gamma
- Indirect action
- By reducing Renin and Modulating RAAS
- Increase calcium flux into the cell which improves transduction pathway
- Increase Osteocalcin production by bone increase adiponectin
- Reduces PTH – higher PTH is associated with insulin resistance
-
Q. What is the link between vitamin D deficiency and diabetic complications?
- Vitamin D deficiency – more complaints of paraesthesia
- Increase urine albumin secretion
- Increase CV risk
-
-
Please consider donating to "Notes in Endocrinology" to keep us going. Please visit our DONATION page to know more